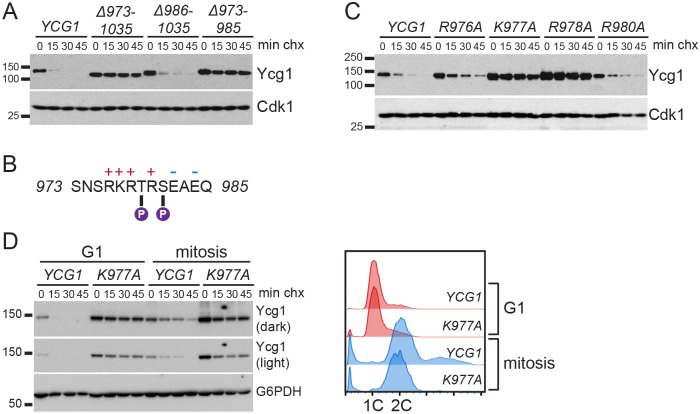
Fig 3. The C-terminus of Ycg1 regulates its degradation.
(A) Cycloheximide-chase assay showing turnover of 3HA-tagged wild-type Ycg1 (YTD33) and the indicated deletion mutants (YTD36, YTD184, YTD128) in asynchronous cells. Also see S1A Fig for an illustration of the mutants. Western blots for HA and Cdk1 (loading control) are shown. (B) Sequence of Ycg1 amino acids 973–985 that regulate Ycg1 stability. Charged amino acids are indicated, as well as T979 and S981 which have been previously shown to be phosphorylated [14]. (C) Cycloheximide-chase assay of strains expressing the indicated 3HA-tagged Ycg1 proteins (YTD33, YTD200, YTD148, YTD201, YTD164) in asynchronous cells. Western blots for HA and Cdk1 (loading control) are shown. (D) YCG1 (YTD33) and ycg1-K977A (YTD148) strains were arrested in G1 with alpha-factor or in mitosis with nocodazole for 3 hours and cycloheximide-chase assays performed. Western blots for HA and G6PDH (loading control) are shown. Flow cytometry plots (right) confirm cell-cycle arrests.