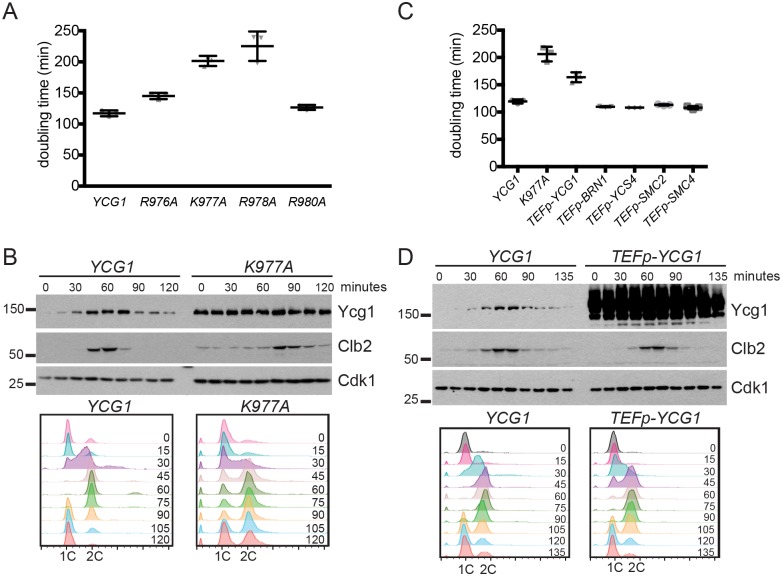
Fig 4. Constitutive expression of Ycg1 delays progression through the cell cycle.
(A) Doubling time of strains expressing the indicated Ycg1 proteins from the endogenous locus (YTD33, YTD200, YTD148, YTD201, YTD164). Mean doubling time from 3 independent experiments, +/- 1 standard deviation, are shown. (B) Strains expressing 3HA-tagged Ycg1 (YTD33) or Ycg1-K977A (YTD148) from the endogenous locus were arrested in G1 with alpha-factor for 3 hours and then released into the cell cycle. Alpha-factor was added back after 45 minutes to prevent cells from entering a second cycle. Western blots of Ycg1-3HA, Clb2 and Cdk1 are shown (top). Flow cytometry plots (bottom) illustrate the delayed progression of ycg1-K977A cells into S phase (compare 30 and 45-minute time points). (C) Doubling time of wild-type (YTD33) and ycg1-K977A strains (YTD148) were compared to strains overexpressing each of the indicated condensin subunits from the TEF1 promoter (YTD336, YTD337, YTD353, YTD349, YTD362). Mean doubling times from 3 independent experiments are shown, +/- 1 standard deviation. (D) YCG1 (YTD276) and TEFp-YCG1 (YTD361) strains were arrested in metaphase with a MET3p-CDC20 shut-off allele for 3 hours, then released into alpha-factor for 2 hours to synchronize cells in G1. Alpha-factor was added back 45 minutes after release from G1 arrest to prevent cells from entering a second cycle. Western blots of Ycg1-3HA, Clb2 and Cdk1 are shown (top). Flow cytometry plots (bottom) demonstrate the delayed progression of ycg1-K977A cells into S phase (compare 30 and 45-minute time points).