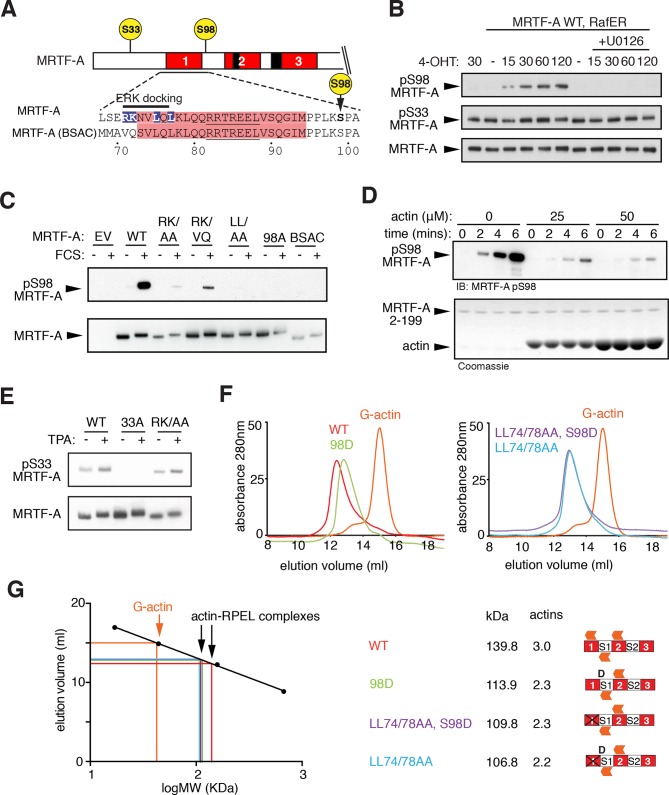
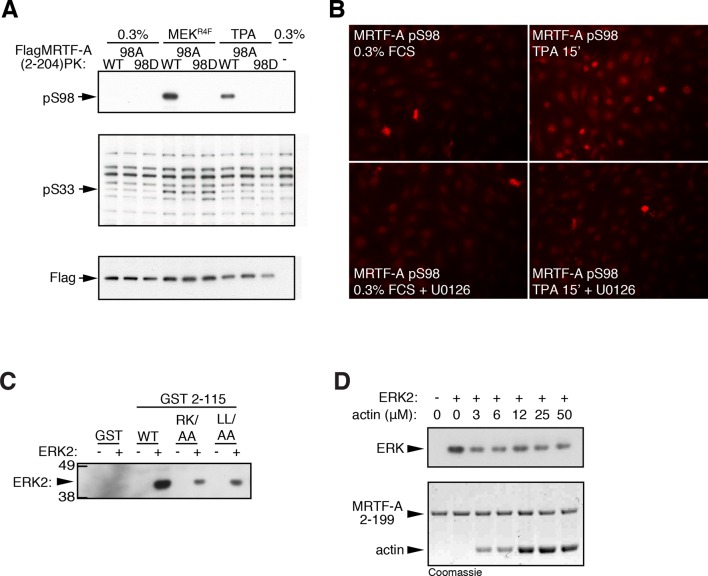
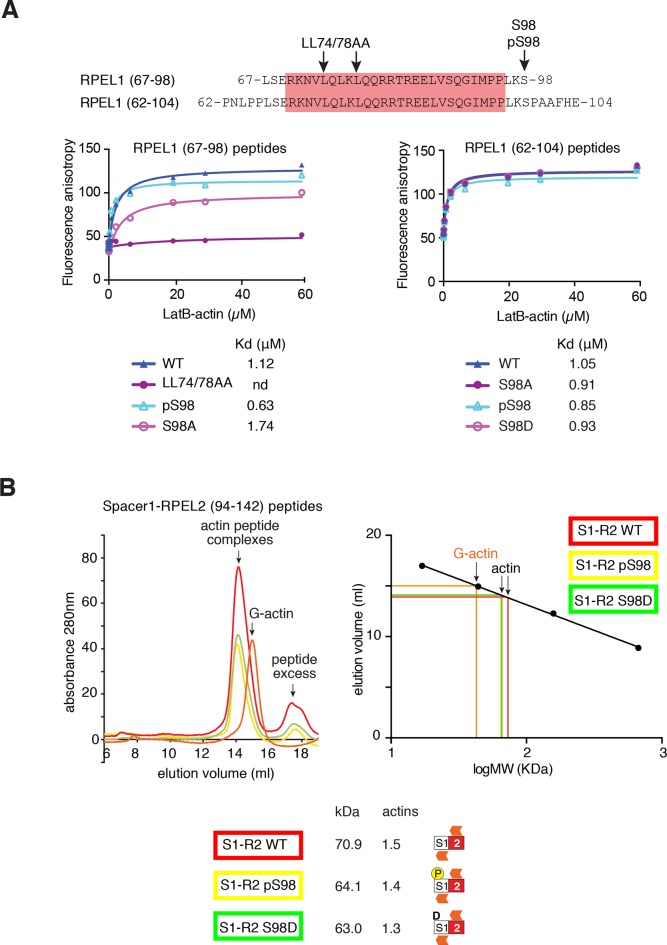
Figure 4. ERK-mediated phosphorylation of S98 inhibits actin binding.
(A) Sequences of MRTF-A(fl) and MRTF-A(BSAC), with RPEL1 highlighted in pink and the ERK-binding motif in blue. (B) Cells expressing Flag-MRTF-A and RafER were treated with 4OHT or vehicle and 10 μM U0126 as indicated. Lysates were analysed by immunoblot for MRTF-A pS98, MRTF-A pS33, and MRTF-A (Flag). (C) Cells expressing wild-type MRTF-A(fl) or derivatives with the indicated ERK-binding site mutations, or MRTF-A (BSAC), were analysed by immunoblotting with MRTF-A phospho-S98 antibody before and after serum stimulation. (D) Phosphorylation of recombinant MRTF-A(2-199) by ERK2 in the absence or presence of G-actin was monitored by MRTF-A phospho-S98 antibody (top) or coomassie staining (bottom). (E) S33 phosphorylation occurs independently of the ERK-binding motif. Cells expressing MRTF-A derivatives were analysed as in (C) using anti-MRTF-A phospho-S33. (F) Size exclusion chromatography of complexes formed between G-actin and recombinant MRTF-A(67–199) derivatives, or G-actin alone, colour coded. (G) Left, calibration curve; right, apparent stoichiometry of G-actin binding.