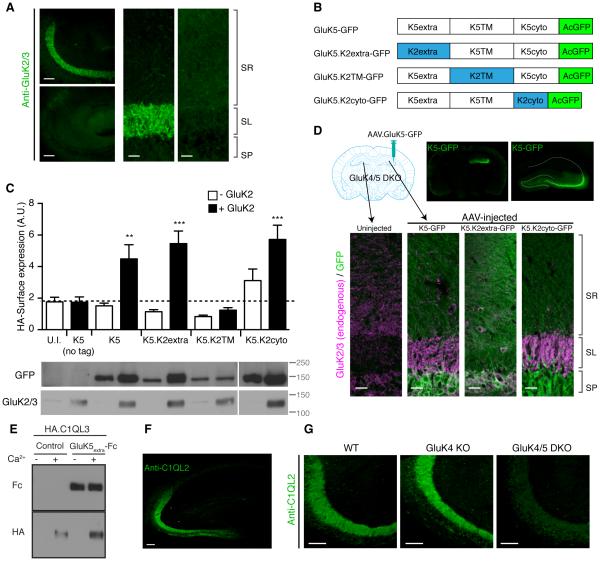
Figure 7. The GluK5 extracellular domain mediates synapse specificity.
(A) Immunostaining of hippocampal sections revealed substantial reduction of GluK2/3 signal in the stratum lucidum layer in GluK4/5 DKO compared to GluK4 KO mice. (B) Schematic diagram of chimeras of GluK5 and GluK2 with GFP at their C-terminus. (C) Surface expression of the extracellularly HA-tagged GluK5-GFP chimeras in cRNA-injected oocytes was measured using chemiluminescence assay. HA-K5-GFP alone did not express at the cell surface. On the other hand, GluK2 co-expression enhanced surface expression of HA-GluK5-GFP, HA-GluK5.K2extra-GFP and HA-GluK5.K2cyto-GFP, but not HA-GluK5.K2TM-GFP (n = 6-8). Expression of chimeric proteins was confirmed by western blotting. (D) Upon stereotaxic injection of AAV carrying GluK5-GFP, GluK5-GFP signal was observed in AAV-injected hemispheres in GluK4/5 DKO hippocampus (top). Re-introducing GluK5-GFP and GluK5.K2cyto-GFP into GluK4/5 DKO restored the stratum lucidum localization of endogenous GluK2 (Magenta), whereas GluK5.K2extra-GFP failed. Composite images were shown. (E) HA-tagged C1QL3/nCLP3 bound to the GluK5 extracellular domain tagged with human Fc domain (GluK5extra-Fc). Two proteins expressed independently were mixed and pulled down with protein A-sepharose. HA-C1QL3 was pulled down with GluK5extra-Fc strongly, but not with bovine serum albumin (control). Addition of calcium (Ca2+) was required for their interaction. (F) Immunostaining of C1QL2/nCLP2 in the hippocampus resulted in a selective distribution at the stratum lucidum, mimicking the distribution pattern of KARs. (G) The stratum lucidum distribution of C1QL2 was markedly reduced in GluK4/5 DKO mice. Data in C are given as mean ± s.e.m. ** P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Scale bars: 100 μm (A, left panels; F, G), 20 μm (A, right panel; D, bottom).