Figure 6.
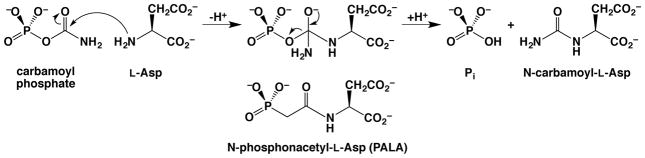
Aspartate transcarbamoylase catalyzes the condensation of carbamoyl phosphate with L-aspartate to yield N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate plus inorganic phosphate (Pi). The bi-substrate analogue N-phosphonacetyl-L-aspartate (PALA) mimics structural features of both substrates and is a potent ATCase inhibitor. The binding of PALA reveals key intermolecular and intramolecular interactions that suggest a catalytic function for the phosphate group (see Figure 7).