Figure 5.
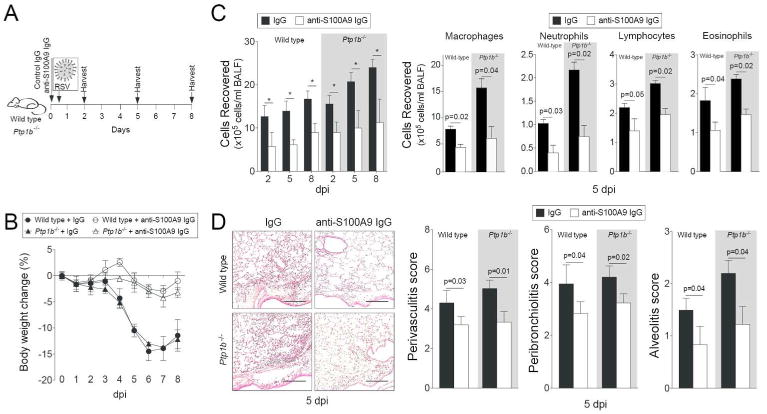
Infiltration of immune cells following RSV-infection is diminished upon neutralization of extracellular S100A9 signaling. (A) Wild type and Ptp1b-/- mice were IP injected with isotype control IgG or anti-S100A9 IgG prior to intranasal infection with 1×106 pfu of RSV and animals were euthanized 2, 5 and 8-days post infections. (B) Animal body weight and (C) BALF cellularity (total BAL cells, macrophages, neutrophils, lymphocytes and eosinophils) were determined in each group (white background = wild type and grey area = Ptp1b-/- mice). (D) Comparative histology images of infected animals 5 dpi are presented here (scale bar=50 μm). Histopathology (Peribronchiolitis, perivasculitis and alveolitis scoring) was recorded in mice for each group. Slides were randomized, read blindly and scored for each parameter. Graphs are represented as mean ± S.E.M., where each measurement was performed 3 times on 10 animals/group. * p < 0.05 or p values shown, comparing both treatments connected by a line.
