Figure 7.
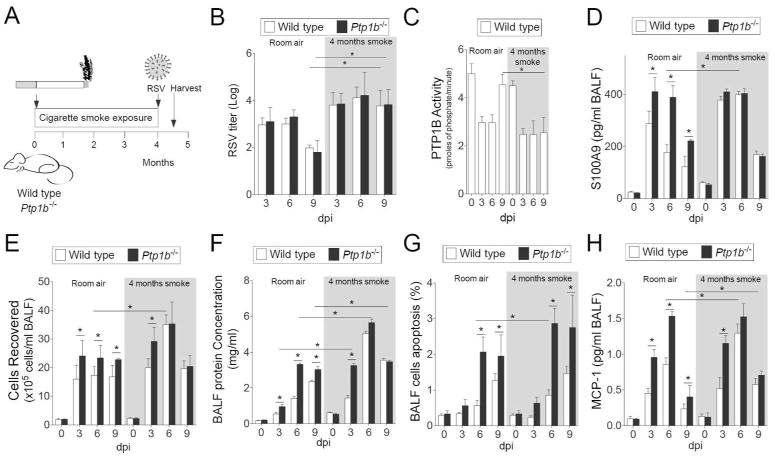
Cigarette smoke exposure enhances RSV infection induced lung damage. (A) Wild type and Ptp1b-/- mice were exposed to cigarette smoke for 4 months prior to intranasal infection with 1×106 pfu of RSV and animals were euthanized 0, 3, 6 and 9-days post infection. (B) Lung RSV titer, (C) lung PTP1B activity, (D) BALF levels of S100A9, (E) BALF cellularity, (F) BALF protein content, (G) BALF cells undergoing apoptosis and (H) BALF MCP-1 levels were determined (white background = room air and grey area = smoke exposed for 4 months). Graphs are represented as mean ± S.E.M., where each measurement was performed on 10 animals/group, with 6 replicates/animal. * p < 0.05, comparing both treatments connected by a line.
