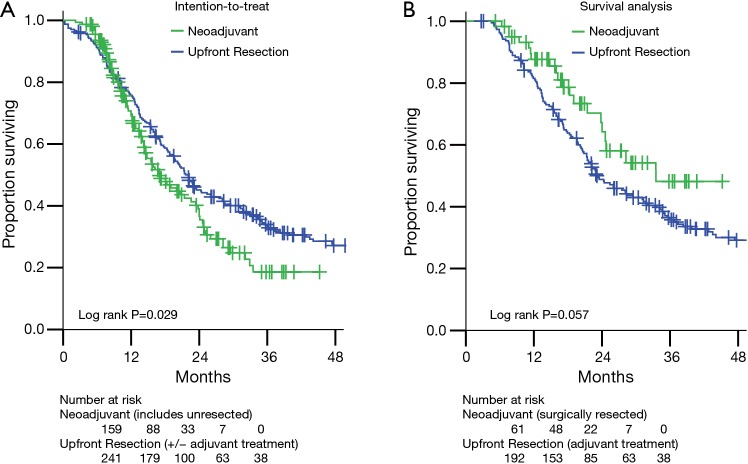
Figure 2.
Actuarial overall survival for the cohorts in this study. (A) The intention-to-treat analysis compares the survival of all 241 upfront resectable pancreatic cancer patients who underwent pancreatectomy without neoadjuvant therapy to all 159 patients not judged to be upfront resectable (110 BRPC and 49 LAPC) who underwent neoadjuvant multi-agent chemotherapy and SBRT with the intention of resection. (B) The survival analysis compares the survival of patients who received the intended therapy. There were 192 upfront resection patients who underwent pancreatectomy followed by standard of care chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy. Sixty-one (56 BRPC and 5 LAPC) patients underwent neoadjuvant multi-agent chemotherapy and SBRT followed by resection. Long-term outcomes after pancreatectomy were not worsened by neoadjuvant therapy. BRPC, borderline resectable pancreatic cancer; LAPC, locally advanced pancreatic cancer; SBRT, stereotactic body radiation therapy.