FIG 1.
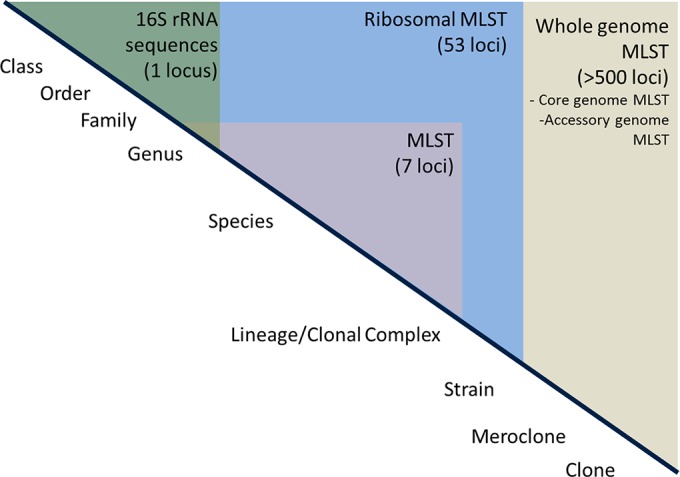
Hierarchical approach to WGS data analysis. The data represent the increasing resolution seen in analyzing different and increasing numbers of loci in bacterial genomes (above the diagonal line, shaded), along with their relationship to nomenclature (below the line). 16S rRNA efficiently identifies bacteria to the genus level, whereas conventional locus MLST (sometimes called multilocus sequence analysis [MLSA]) enables resolution within genera and species. The 53-locus rMLST approach allows species identification and resolution within species, while the highest levels of resolution are obtained with whole, core, and/or accessory genome MLST. (Image republished from reference 5 with permission of the publisher.)
