FIG 2.
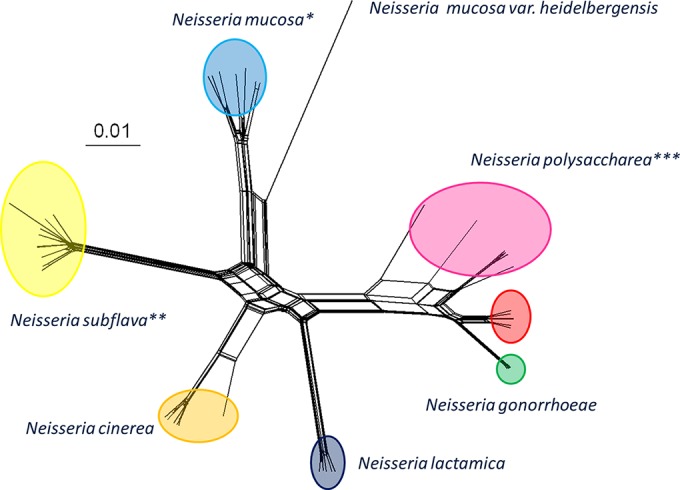
Evolutionary relationships among Neisseria species based on concatenated sequences of the 53 ribosomal gene proteins (rMLST). The relationships among different Neisseria species were reconstructed with nucleotide sequences from 49 ribosomal gene proteins. Single asterisks (*) denote a cluster of Neisseria mucosa species in which isolates previously identified as being Neisseria sicca and Neisseria macacae species were found, indicating that rMLST analysis had identified these as being variants of the N. mucosa species. Double asterisks (**) denote a cluster composed of Neisseria subflava species in which isolates previously identified as Neisseria flavescens had clustered. Triple asterisks (***) denote a polyphyletic group comprising N. polysaccharea isolates indicative of the presence of more than one N. polysaccharea species. (Image republished from reference 6with permission of the publisher.)
