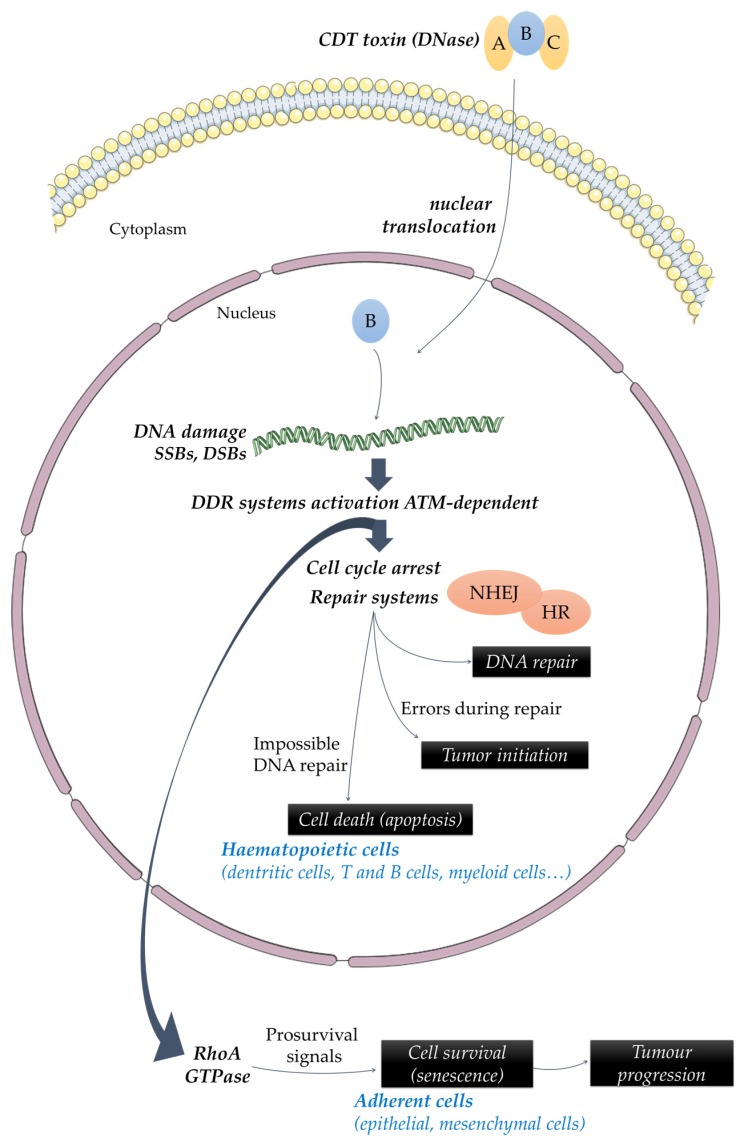
Figure 2.
Impact of CDT-producing bacteria on cellular physiology. As a result of DSBs caused by CDT-intoxication, DNA repair mechanisms are activated, among them, DNA damage response (DDR) including homologous recombination (HR) and non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) mechanisms. In some cases, the DDR system fails to properly repair DNA damage, leading to cell death by apoptosis in hematopoietic cells. In adherent cells, the presence of pro-survival signals (RhoA GTPase and p38) leads to cell cycle arrest and senescence. Errors made during DNA repair could favor tumor initiation whereas a senescent state could play a role in tumor progression. A, B and C represent the CDT subunits.