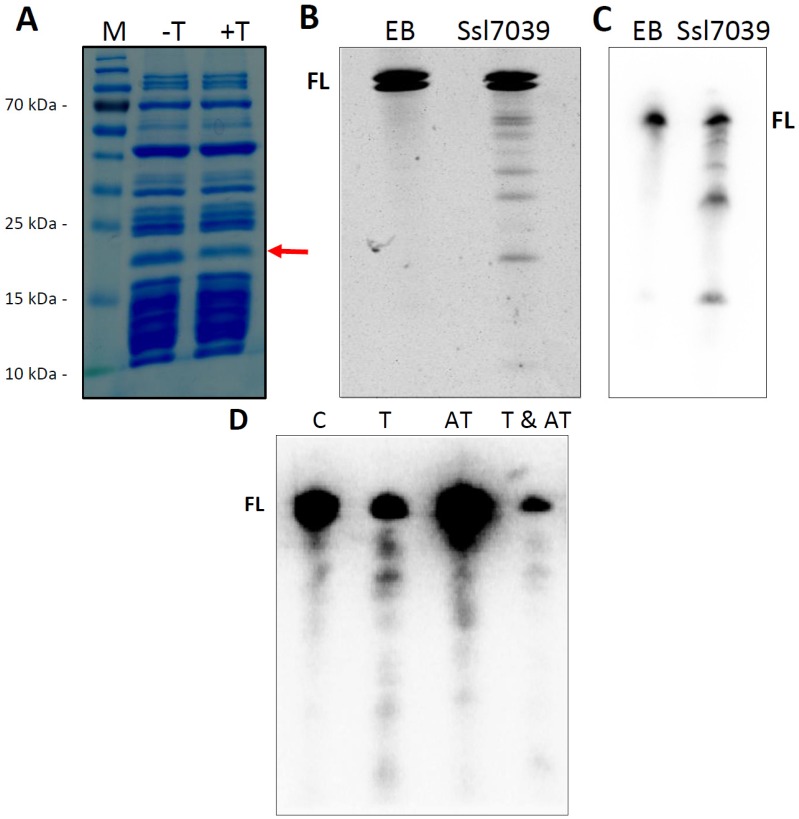
Figure 6.
Purified toxin Ssl7039 exhibits ribosome-independent RNase activity. (A) Addition of Ssl7039 to the coupled transcription-translation approach, expressing the DHFR control template, decreases DHFR protein abundance. The DHFR band is labeled by an arrow. The synthesis reaction were separated on 10% SDS–PAA gel electrophoresis and visualized by Coomassie staining. M, marker (PageRuler, Thermo Fisher Scientific); -T, no addition of purified Ssl7039; +T, addition of purified Ssl7039. (B) In vitro synthesized dhfr mRNA was incubated for 30 min with purified toxin Ssl7039, resulting in a clear cleavage pattern. Incubation with elution buffer (EB) served as control. The reaction were separated on 6%–10% 7 M urea polyacrylamide gels (6 mA, 1.5–2.5 h) and visualized by ethidium bromide staining. FL, full length dhfr mRNA (~500 nt). (C) Total RNA from the coupled transcription/translation approach was extracted 2 h after toxin addition, followed by northern analysis targeting the dhfr mRNA. EB, elution buffer control; Ssl7039, addition of purified Ssl7039. (D) Expression of Ssl7039 decreases lpp mRNA stability in vivo. The expression strain E. coli Bl21 (DE3) Rosetta, harboring the plasmid pET28a(+)::ssl7039 and pBAD::ssl7038, was grown in LB medium to an optical density (O. D.) of 0.3–0.4 and then split before addition of the appropriate inducer. Total RNA was extracted 30 min after inductor addition, followed by northern analysis aimed at the lpp mRNA. FL, full length lpp transcript; C, no inducer; T, toxin expression; AT, antitoxin expression; T & AT, both toxin and antitoxin expression.