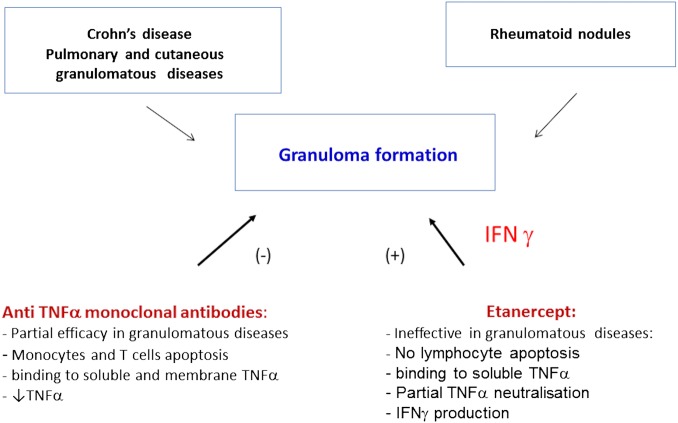
Figure 6.
Mechanisms involved in aseptic granulomatous diseases occurring with anti–TNF-α therapy. Anti–TNF-α monoclonal antibodies and the p75 soluble TNF-α receptor have differential immunological properties that may be associated with granuloma formation and thus with the development of granulomatous diseases. Indeed, anti TNF-α monoclonal antibodies induce profound TNF-α inhibition, whereas etanercept partially respects the production of this cytokine. Etanercept is associated with IFN-α production, which contributes to granuloma formation, while anti–TNF-α monoclonal antibodies inhibit IFN-γ release. IFN-α, interferon α; TNF-α, tumour necrosis factor α.