Fig. 4.
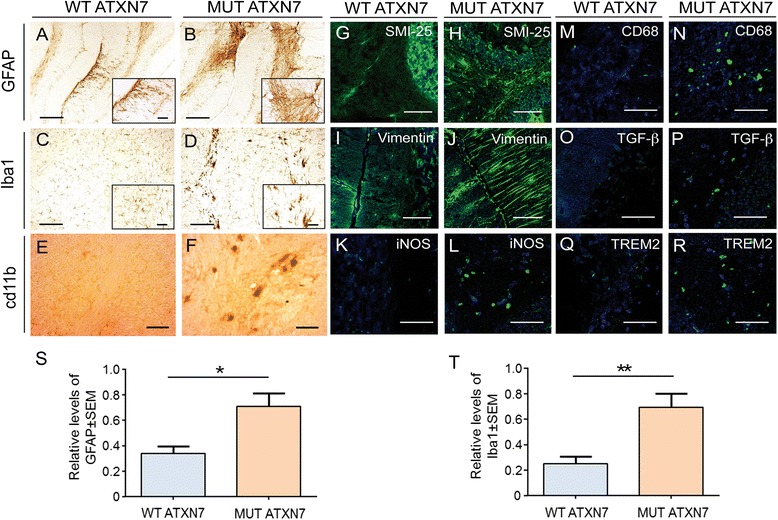
Cerebellar overexpression of MUT ATXN7 induces immunoreactivity of markers of inflammation. a–f Cerebellum injected with LV-MUT-ATXN7 shows increased GFAP (B), Iba1 (microglia) (D) and cd11b (F) immunoreactivity compared to a cerebellum injected with WT ATXN7 (A, C and E, respectively). g–r Laser confocal microscopy shows increased astrocytic immunoreactivity (SMI-25 staining; green) in cerebellar regions transduced with MUT ATXN7 (H) compared to control regions injected with WT ATXN7 (G); Anti-vimentin staining (green) shows increased immunoreactivity of Bergmann glial cells in the cerebellar ML transduced with MUT ATXN7 (J) relatively to the ML transduced with WT ATXN7 (I). The increased immunoreactivity of the microglial markers NOS2 (L), CD68 (N), TGF-ß (P) and TREM2 (R) (in green) is observed in cerebellar regions overexpressing MUT ATXN7, compared to regions overexpressing WT ATXN7 (K, M, O and Q, respectively). s and t Quantification showing increased GFAP-positive immunoreactivity (S) and Iba1-positive immunoreactivity in the cerebellum of mice injected with LV encoding MUT ATXN7 (n = 4), relatively to WT ATXN7-injected mice (n = 4); Student’s T test. Values are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Bars: A–D: 200 μm; E and F: 50 μm; G–J: 50 μm; K–R: 20 μm
