Fig. 1.
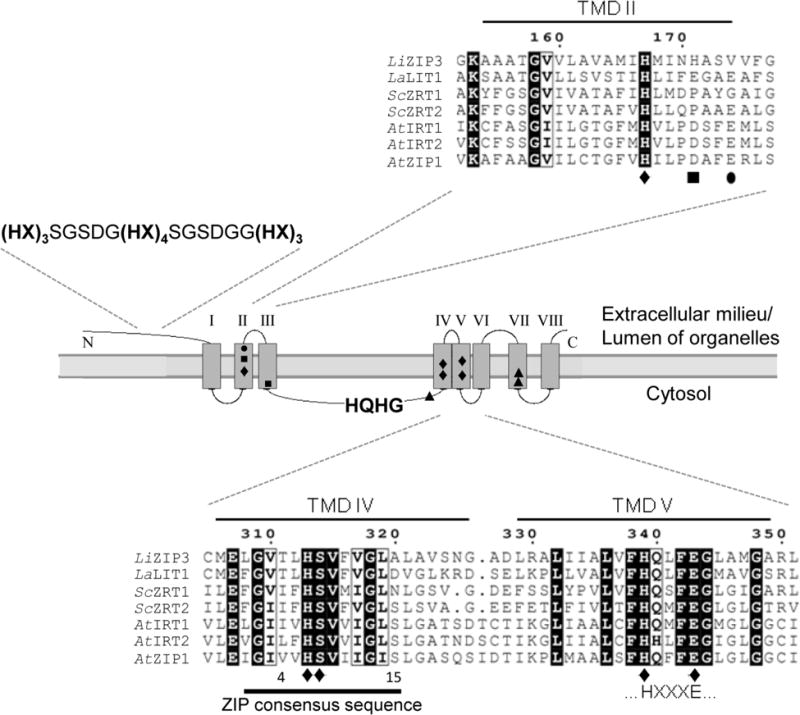
LiZIP3 is predicted to encode a member of the ZIP family. Alignment of selected residues of the predicted amino acid sequence of LiZIP3 with experimentally characterized ZIP members from L. amazonensis (La), S. cerevisiae (Sc) and A. thaliana (At) using MultAlin interface (Corpet, 1988). Also depicted is the topology of LiZIP3 predicted with TopPred 0.01 (Claros & von Heijne, 1994). Highlighted are the LiZIP3 transmembrane domains (TMDs) and the residues shown to be important for transport of zinc (●), of iron, manganese, zinc and cadmium (◆), and of iron and manganese (■) in AtIRT1, and of iron (▲) in LaLIT1. Histidine-rich regions, the ZIP consensus sequence and the HXXXE motif, characteristic of ZIP members, are also represented. Accession numbers: LiZIP3, LinJ.28.2050; ScZRT1, CAA96975.1; ScZRT2, CAA97701.1; AtIRT1, NP_567590.3; AtIRT2, NP_001031670.1; AtZIP1, NP_187881.1; LaLIT1 sequence was obtained by modification of the L. major orthologue LmjF.31.3060 according to Huynh et al. (2006).
