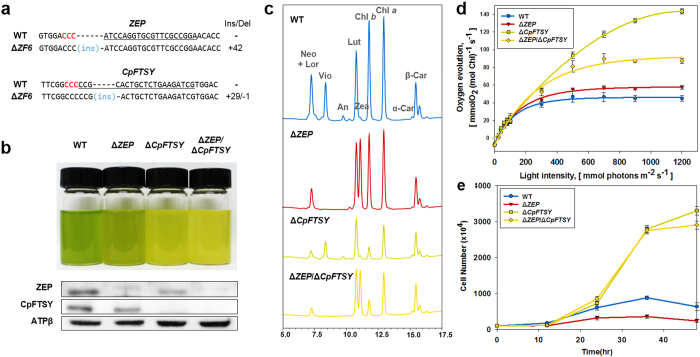
Figure 3. The sequential CpFTSY and ZEP two-gene knockout mutants by transfecting RGEN-RNPs.
(a) Targeted indel mutations induced by RGEN RNPs at the ZEP and CpFTSY gene in the ΔZEP/ΔCpFTSY double mutant. (b) Phenotype of wild type, ΔZEP, ΔCpFTSY and ΔZEP/ΔCpFTSY mutants of C. reinhardtii. Cells were grown photoautotrophically under high-light (500 μmol photons m−2 s−1) conditions. Cell densities were 10 × 106 cells/mL. Western-blot analysis of the ZEP and FTSY proteins in the wild type (WT) and the RGEN-induced transgenic lines. Immuno-detection of proteins with the β-subunit of ATP synthase (ATPβ) of Chlamydomonas was used as the loading control of the samples. (c) HPLC profiles of total pigments from acetone extracts of wild type(blue), ΔZEP(red), ΔCpFTSY(green) and ΔZEP/ΔCpFTSY double mutant(yellow). Lor, Loroxanthin; Neo, neoxanthin; Vio, violaxanthin; An, antheraxanthin; Lut, lutein; Zea, zeaxanthin; Chl b, Chlorophyll b; Chl a, Chlorophyll a; α-Car, α -carotene; β-Car, β-carotene. (d) Light-saturation curves of photosynthesis in wild type (blue) and ΔZEP (red), ΔCpFTSY (green) and ΔZEP/ΔCpFTSY (yellow). Rates of oxygen evolution on a per Chl basis were measured as a function of incident light intensity. (e) Growth curve of wild type and the mutants lines cultured in HS medium at 25 °C with air containing 5% CO2 under High light (700 μmol photons m−2 s−1).