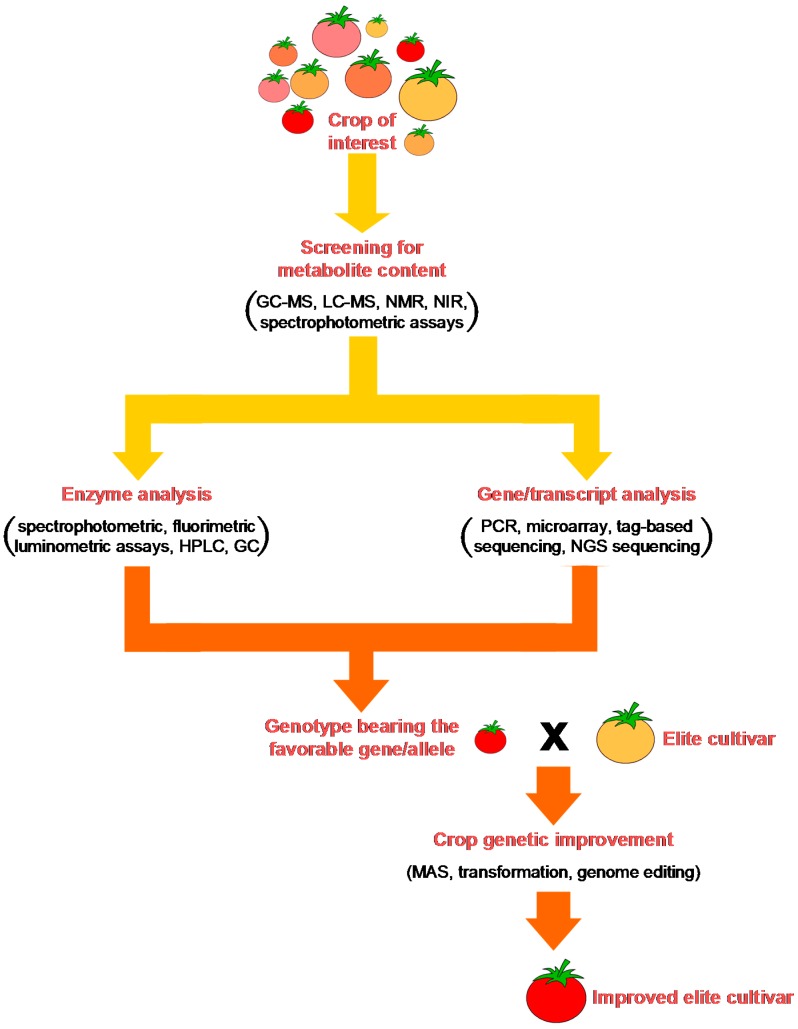
Figure 5.
Outline of how a functional approach can contribute to identification of a candidate gene associated with high levels of a health-promoting phytochemical in a staple crop. A germplasm collection is screened to determine the variability in nature of the trait. Genotypes characterized by contrasting metabolite accumulation are subjected to enzymatic analysis to identify key enzyme variants (i.e., allozymes) that are characterized by contrasting activities/efficiencies, and molecular analysis to identify alleles that encode the different allozymes and to evaluate their expression levels. Then, on the basis of both the enzymatic and molecular information, a candidate gene/allele can be identified that can then be efficiently used in advanced breeding programs that are aimed at the introgression of the trait of interest into an elite cultivar.