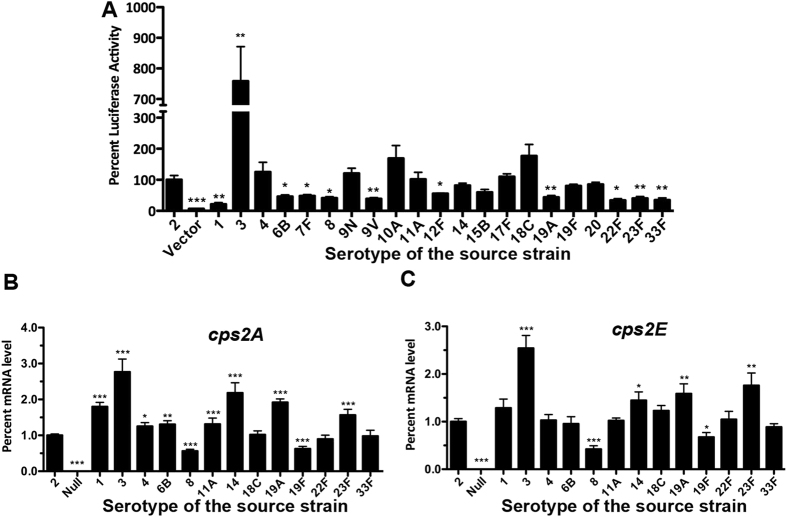
Figure 3. Transcriptional activity from the promoter sequence for each of the 22 major IPD serotypes.
(A) Assessment of promoter activity by a luciferase reporter. Each promoter sequence was fused to the 5′ end of a promoterless luciferase gene in the pIB166 shuttle plasmid, and transformed in strain D39. The promoterless plasmid (vector) was used as a negative control. Transcriptional activity of each cps promoter sequence was quantified by measuring luminescence level of the mid-log culture inoculated with the pneumococci carrying the appropriate reporter construct. Each reporter was identified with the serotype of its source strain. The sequence of the first strain was used for each of the serotypes with multiple strains listed in Fig. 1. The values represent the percent luciferase activities of the reporters relative to the luciferase activity readout of the D39 (first bar) promoter construct. (B) The qRT-PCR readouts of the cps2A transcripts from the promoter replacement D39 derivatives of 13 IPD serotypes. The promoterless derivative TH4525 described in our previous study was used as a negative control. The mRNA levels were presented as relative values to that of D39s. (C) Same as panel B, except that cps2E was tested. The sequence of the first strain was used in both the luciferase and promoter replacement experiments for each of the serotypes with multiple strains listed in Fig. 1. The values were the means ± standard errors of the results from triplicate samples as compared with those of the type 2. *p < 0.05, **<0.01 and ***<0.001.