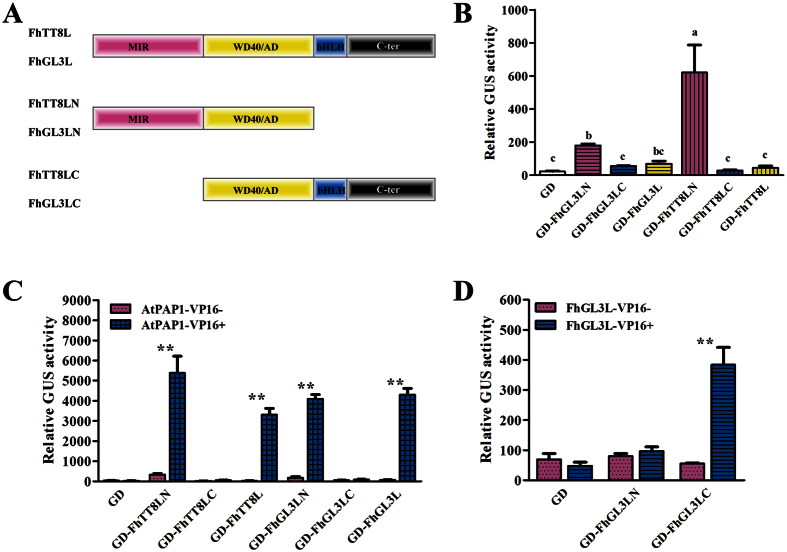
Figure 2. Function of Different Regions of FhGL3L and FhTT8L.
(A) Schematic diagram of the full-length and partial truncated FhbHLHs. (B) Transactivation capacity of different domains of FhbHLHs. (C) Different truncated FhbHLH peptides showed different interaction capacity with AtPAP1. The N-terminal region was indispensable for the interaction with MYB partners. (D) The C-terminal region of FhGL3L was indispensable in dimerization. Activation of GAL4 by the respective constructs was determined by measuring beta-glucuronidase activity. The plasmids were co-transfected into protoplasts isolated from Arabidopsis rosette leaves. Protoplasts were incubated in darkness for 20–22 h after transfection, and then GUS activity was measured. Data represented the mean ± SD of three replicates. Constructs were diagrammed at the bottom of the figure. One-way ANOVA was carried out to compare statistical differences in Fig. 5B. (Ducan, p < 0.05). T-test was used to analysis the significant defference in Fig. 5C,D (*P < 0.05; **p < 0.01). All tests were computed using SPSS(ver.17.0).