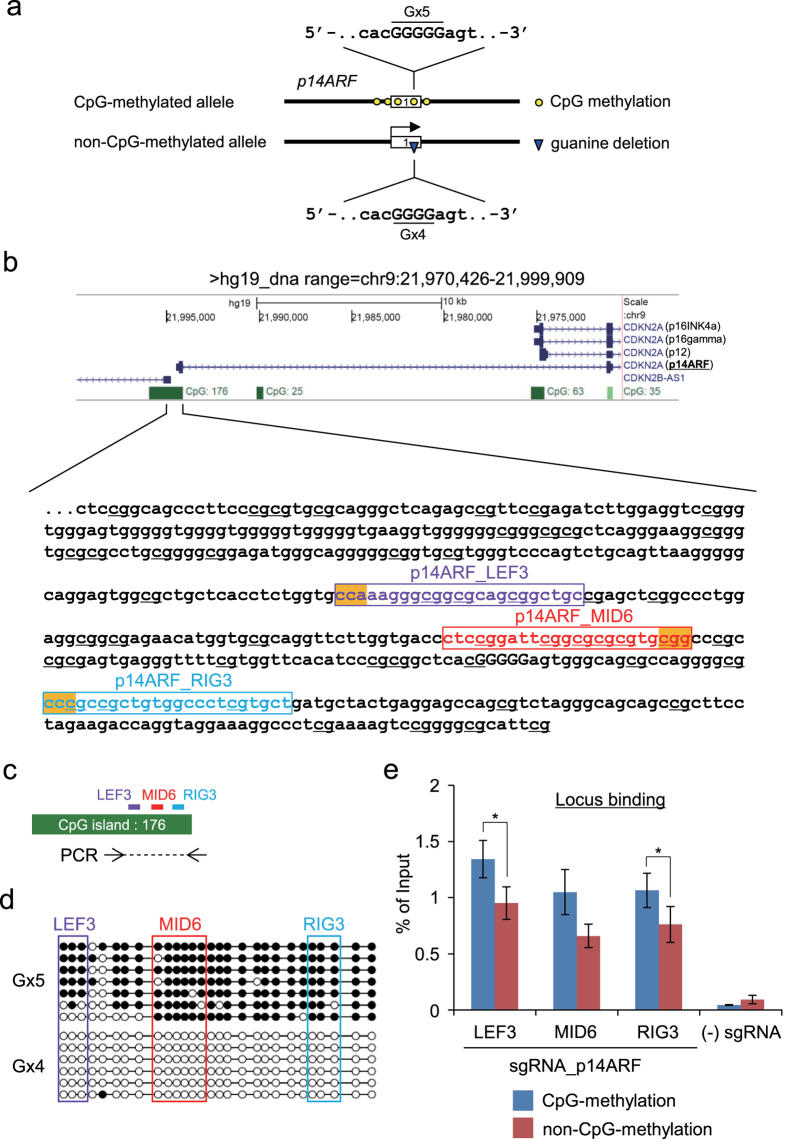
Figure 4. Evaluation of p14ARF locus binding by CRISPR in vivo.
(a) Structure of the human p14ARF gene in HCT116. One allele of the human p14ARF gene is not transcribed in HCT116 because the CpG island (including the promoter region and first exon) is CpG-methylated. In the other allele, a frameshift mutation caused by deletion of a single guanine in the coding region of the first exon prevents production of the functional protein. (b) The CpG island of the p14ARF gene in HCT116. (Upper) Schematic diagram of the CpG island around the first exon of p14ARF. The CpG islands are shown in green. (Lower) A partial DNA sequence of the CpG island (CpG: 176) in the methylated allele. A guanine (G) is deleted from the G stretch (shown in uppercase) of the non-methylated allele. The upper image and DNA sequence were generated using the UCSC Genome Browser (https://genome.ucsc.edu/). CpG sites are underlined. The target sites for sgRNA_p14ARF_LEF3, sgRNA_p14ARF_MID6, and sgRNA_p14ARF_RIG3 are shown in purple, red, and light blue, respectively. PAMs are shown in yellow. (c) Primer positions for bisulfite sequencing. (d) Bisulfite sequencing of genomic DNA extracted from HCT116. Target sites for sgRNAs are constitutively CpG-methylated in an allele-specific manner. (e) DNA yields of conventional enChIP. enChIP targeting p14ARF was performed similarly to Supplementary Fig. S3a. Error bars represents s.e.m. of three enChIP experiments (*t-test P-value < 0.05).