FIGURE 2.
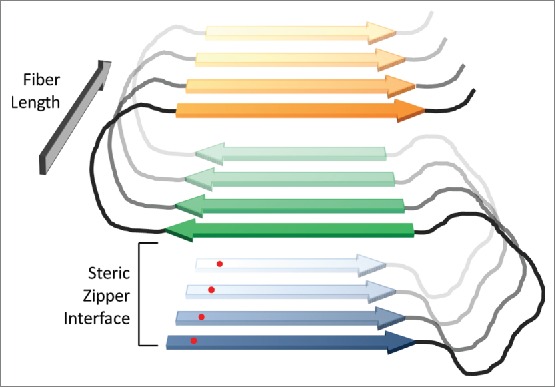
In-register parallel β-sheet structure for prion fibers. In prion fibers, yeast prion proteins are proposed to adopt a serpentine structure, with β-strands (blue, green and orange) separated by loops (black). Protein monomers then stack in-register, forming parallel β-sheets that run the length of the fiber. The fibers are stabilized by both β-sheet interactions along the length of the fiber and steric zipper packing interactions between strands within the plane of the fiber (between the blue and green strands, and the green and orange strands in the figure). Because an individual amino acid (red dot) will align with the corresponding amino acid in the adjacent protein, interactions along the length of the fiber should be largely primary-sequence independent. However, the steric zipper packing interactions should be sensitive to primary sequence.
