Figure 3.
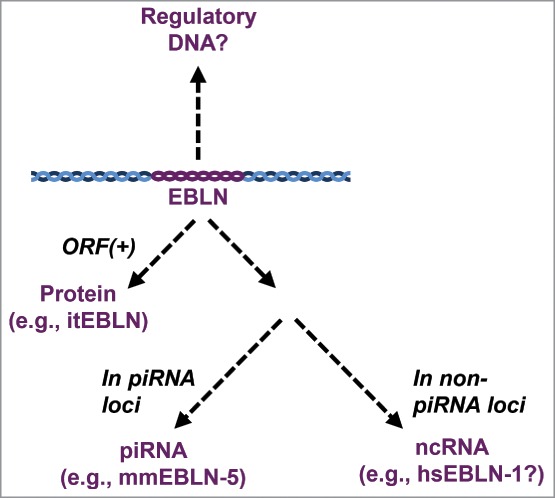
Categorization of EBLN characteristics and functions. The functional mechanisms of EBLNs can be categorized in terms of their characteristics as follows: a regulatory DNA, a functional protein, and a functional ncRNA. All EBLNs can potentially regulate surrounding genes. EBLNs with ORFs may function as functional proteins, such as the case of itEBLN acting as a dominant negative protein. If EBLNs locate within piRNA clusters, these may produce piRNA targeting related exogenous viruses (e.g., mmEBLN-5). Even if EBLNs do not contain ORFs and locate within piRNA clusters, EBLNs can still function as ncRNAs as proposed for hsEBLN-1.
