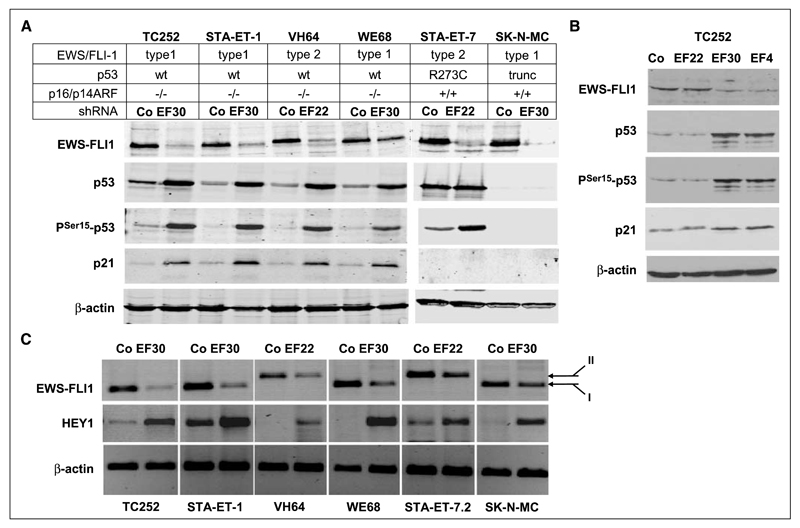
Figure 1.
EWS-FLI1 silencing induces expression of activated p53, p21WAF1/CIP1, and HEY1 expression in wild-type p53 ESFT cell lines. A, p53, PSer15-p53, and p21WAF1/CIP1 accumulation after EWS-FLI1 silencing in four wt-p53 and two mt-p53 ESFT cell lines. Immunoblot analysis 4 d after transfection of the indicated shRNA expression vectors, demonstrating induction of Ser 15-phosphorylated p53 and p21WAF1/CIP1 restricted to the wt-p53 cell lines upon introduction of shRNA specific for the respective EWS-FLI1 fusion types (EF30 for type 1 EWS-FLI1 in TC252, STA-ET-1, WE68, and SK-N-MC cells; EF22 for type 2 EWS-FLI1 in VH64 and STA-ET-7.2 cells) compared with control transfections with a nontargeting shRNA (Co). β-Actin is shown as a loading control. B, p53, PSer15-p53, and p21WAF1/CIP1 accumulation are specifically associated with EWS-FLI1–modulating shRNAs. TC252 cells were transfected with either nontargeting shRNA, shRNAs targeting the EWS-FLI1 type 1 fusion region (EF30) or the FLI1 3′ portion (EF4), or with a shRNA to the type 2 fusion region as a mismatched control. EWS-FLI1 and p53 protein expression was monitored by Western blotting. C, demonstration of HEY1 induction upon EWS-FLI1 silencing by RT-PCR 96 h after EWS-FLI1 silencing. For control, a nontargeting shRNA was transfected. β-actin PCR was used as a control for equal input. EWS-FLI1 fusion types I and II are indicated.