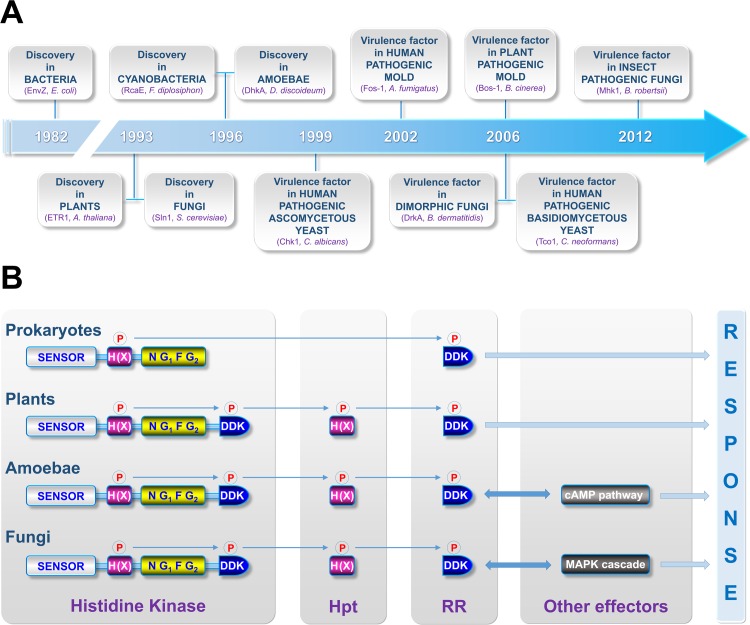
Fig 1. Milestones in the discovery of histidine kinases (HKs) and currently accepted canonical signaling pathways involving HKs in prokaryotes, plants, amoebae, and fungi.
(A) Historical timeline depicting the evolution of knowledge concerning HKs. In the order of appearance from left to right: the EnvZ osmosensor in Escherichia coli [1], the phytohormone ethylene receptor ETR1 in Arabidopsis thaliana [2], the Sln1 osmosensor in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [3], the RcaE cyanobacteriochrome [5], the discadenine receptor DhkA in Dictyostelium discoideum [6], the quorum sensing-associated Chk1 in Candida albicans [26], the virulence factor Fos-1 in Aspergillus fumigatus [27], the dimorphism-related Drk1 in Blastomyces dermatitidis [28], the Bos-1 osmosensor in Botrytis cinerea [29], the Cryptococcus neoformans Tco1 and Tco2 (a first functionally characterized dual HK) [30], and the Metarhizium robertsii Mhk1 [31]. (B) Canonical schemes depicting signaling pathways involving HKs in prokaryotes, amoebae, plants, and fungi. In prokaryotes, most signaling pathways involving HKs simply consist of two components. The perception of a stimulus by the sensor domain (grey box) induces the autophosphorylation of a conserved histidine (H, pink box) by the catalytic domain (N G1 F G2, yellow box) in the HK. The phosphate is then transferred to a conserved aspartate residue (D) located on a cytosolic response regulator (RR) and the activated RR governs the expression of response genes. In plant cells, most (but not all) HKs constitute the initial sensing proteins of a four-step phosphorelay signaling pathway involving phosphorylation events of two downstream elements, i.e., histidine phosphotransfer shuttle proteins (Hpt) and RRs. Note that a first phosphorylatable receiver domain (DDK) is fused to the catalytic domain (N G1 F G2) in the HK. As observed for the archetypal two-component system in prokaryotes, the activated RR governs the expression of response genes. In amoebae, similarly to plants, a four-step phosphorelay signaling pathway is observed, but this latter controls a downstream cyclic AMP pathway. Finally, in fungi, knowledge is very fragmented, but initial studies in Saccharomyces cerevisiae have demonstrated that HKs also constitute the initial sensing proteins of a four-step phosphorelay signaling pathway that governs a cascade of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases.