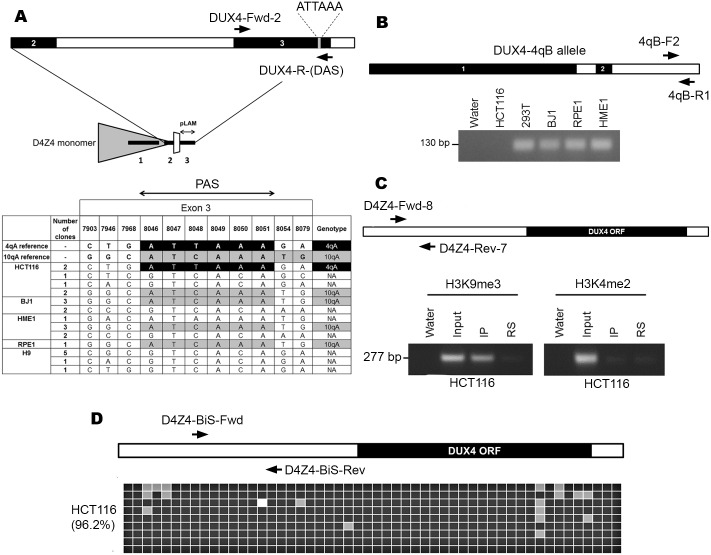
Fig 1. Genotyping and characterization of HCT116 at D4Z4.
(A) Top panel depicts the primer map for genotyping the poly-A signal that stabilizes DUX4 transcripts. A single D4Z4 monomer (grey triangle) containing exons 1, 2 and 3 (thick black lines) of DUX4, along with the pLAM region is shown below, with the region spanning exons 2 and 3 (interrupted by Intron 2 in white) expanded on top. Arrows indicate location of primers for genotyping PCR. Genotyping results in the bottom panel indicate cell lines surveyed and number of clones observed for each haplotype. The numbers on top indicate the positions in base pairs that correspond to single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) characteristic of 10qA and permissive 4qA alleles in this region based on Accession Numbers AL732375 and FJ439133, respectively. The reference permissive 4qA allele containing poly-A signal ATTAAA (black) and 10qA (grey) are indicated (first two rows) and matches are represented likewise for the samples. Non-matching sequences are annotated as not assigned (NA). (B) Labeled arrows show location of primers at the distal edge of D4Z4 that were used to detect 4qB alleles. A representative image of an ethidium bromide–stained agarose gel showing PCR results is depicted below with cell lines indicated above. Product size indicated on the left. (C) Labeled arrows show location of primers, relative to the DUX4 ORF (black rectangle) within each D4Z4 monomer (open rectangle) for PCR of ChIP samples. Immediately below is a representative image of ethidium bromide–stained agarose gels showing PCR results for HCT116 ChIP with anti-H3K9me3 (left) and anti-H3K4me2 (right). Product size is indicated on the left. Samples include water, input, ChIP elution (IP), and a rabbit serum (RS) control. (D) Labeled arrows show location of primers, relative to the DUX4 ORF (black rectangle) within each D4Z4 monomer (open rectangle). Result of bisulfite analysis for 52 CpG sites in HCT116 (average percentage methylation value shown on the left within brackets) within D4Z4 is shown below. Methylated cytosines are represented by black squares whereas unmethylated ones are colored grey. DNA variants that result in a sequence that is no longer a CpG are colored white. Each row of squares represents DNA sequence obtained from an independent single clone.