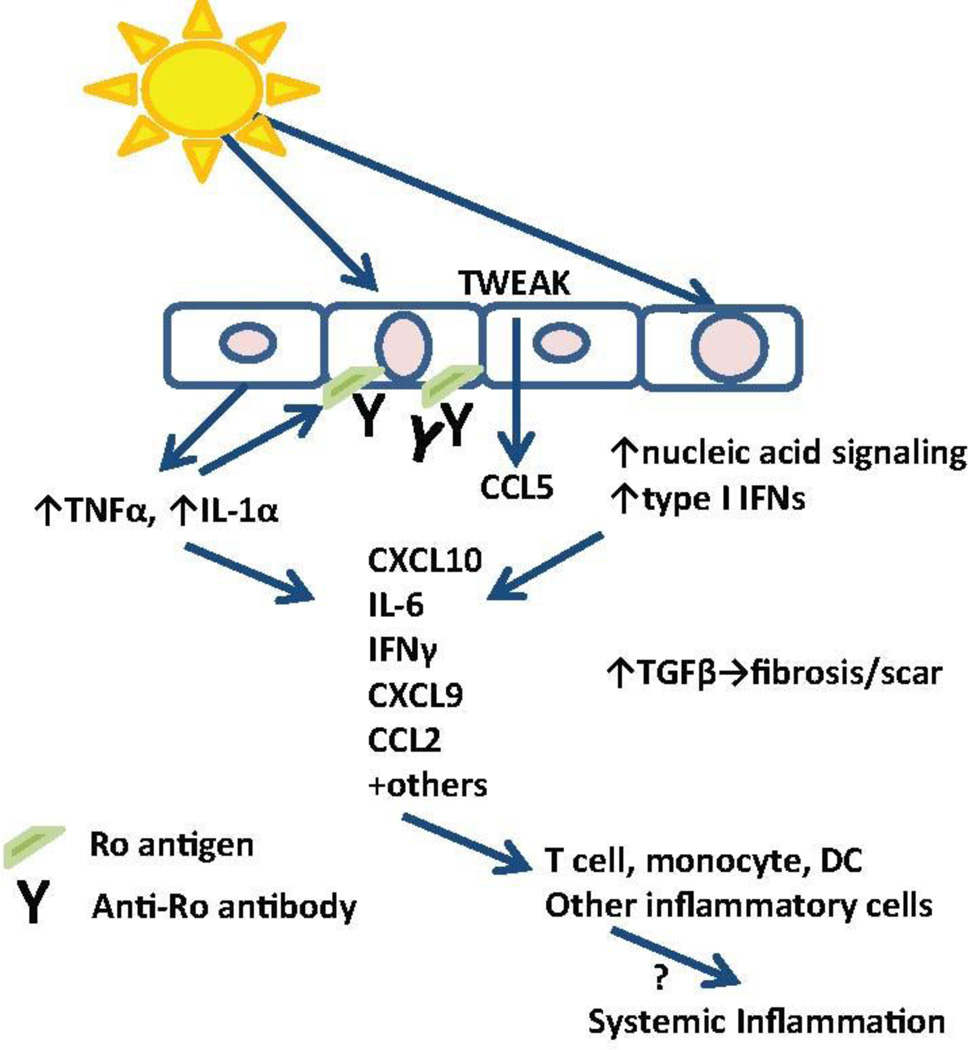
Figure 1. Summary of CLE pathogenesis.
Triggers for skin inflammation, including UV light, stimulate innate cytokine production from keratinocytes and trigger cell death which can activate nucleic acid signaling pathways. Increased autoantigen exposure on the cell surface encourages immune complex deposition, which can lead to antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Cytokine and chemokine production promotes inflammatory infiltrates which damage tissues, perpetuate the inflammatory cycle and lead to chronic TGFβ signaling which promotes damage and scar. The links between skin inflammation and systemic disease require further study. DC=dendritic cell