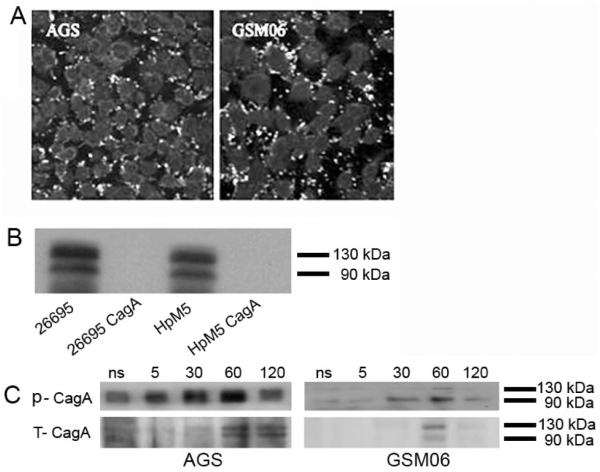
Figure 1.
H. pylori associates with mouse gastric GSM06 epithelial cells and translocates CagA. (A) Epithelial cells grown on glass coverslips were infected with HpM5, washed, fixed, and stained with H. pylori-specific mouse antisera and anti-mouse IgG-FITC conjugate. Cellular morphology was detected using phalloidin and DAPI counter-stains. (B) Western blot analysis of bacterial lysate from strain 26695, 26695 with a PAI deletion (26695 CagA), mouse-adapted HpM5 and the isogenic mutant HpM5 aph::cagA (HpM5 CagA) using anti-CagA polyclonal antibody. (C) CagA-specific immunoblot analysis of AGS and GSM06 cell lysates following infection with HpM5 demonstrating phospho-CagA (P-CagA) and total CagA (T-CagA).