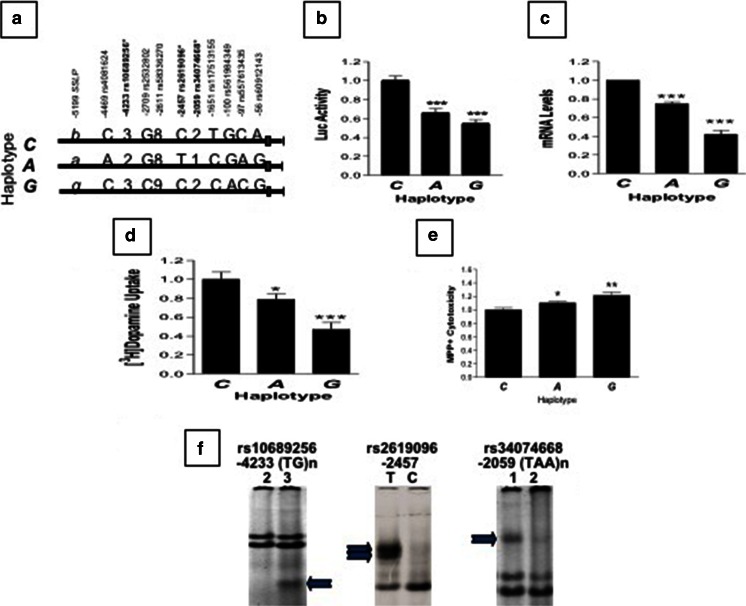
Fig. 2.
Negative correlation between promoter activities and methylpiperidinopyrazole iodide (MPP+) cytotoxicity conferred by 3 haplotypes (C, A, G) of the 6.3-kb hVMAT2 promoter region in SH-SY5Y. (A) Allelic differences among 3 promoter haplotypes, with markers indicated on top. Asterisk indicates 3 haplotypes associated with Parkinson’s disease by family study (Table 2). (B) Three haplotypes showed various promoter activities, based on luciferase (Luc) reporter (***p < 0.001 by Student’s t tests, compared with haplotype C. Three haplotypes drove hVMAT2 mRNA expression (C) or [3H]dopamine uptake activities (D) at levels consistent with Luc activities in (B), based on quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction). ### p < 0.001 compared with C, based on ANOVA analysis. (E) Low activity-associated hVMAT2 promoter confers high MPP+ cytotoxicity. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 by t tests, compared with C. Cells transiently expressing 6.3kb-cDNA hybrids were treated with 0.1 mM MPP+ for 3 days, followed by cytotoxicity analysis using CytoTox-ONE Homogeneous Membrane Integrity Assay (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). (F) Three associated hVMAT2 promoter polymorphisms showed allele-dependent binding activity (indicated by arrows) by nuclear proteins isolated from SH-SY5Y, based on electrophoretic mobility shifting assay. Two non-single nucleotide polymorphisms are at –4233 base pairs (bp) (n = 2/3) and at –2059 bp (n = 1/2)