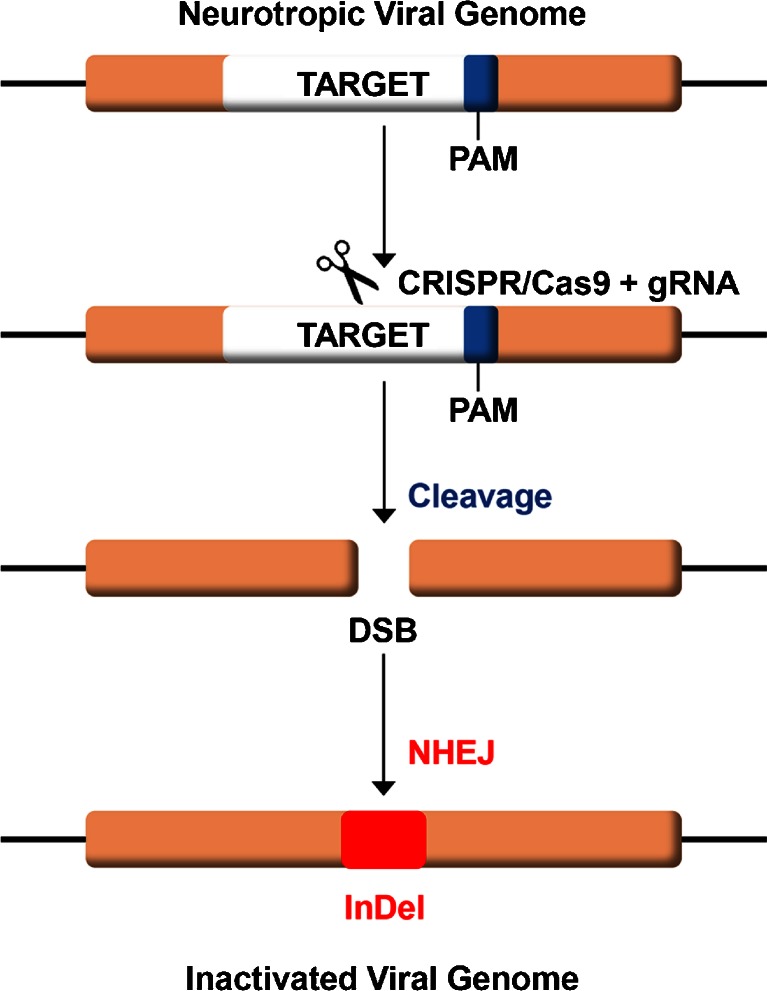
Fig. 1.
Schematic of clustered regulatory interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated 9 (Cas9) action on viral DNA. A guide RNA (gRNA) is designed that is specific for a target sequence immediately adjacent to a 3’ protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequence (blue) within the genome of the virus. The gRNA is expressed in host cells together with the Cas9 endonuclease, which are shown schematically as scissors. CRISPR cleaves the viral DNA at the target site resulting in a double-strand break (DSB), which is repaired by nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ). As NHEJ is error prone, small insertions and deletions (InDel) are found in the repaired DNA that inactivate the target gene