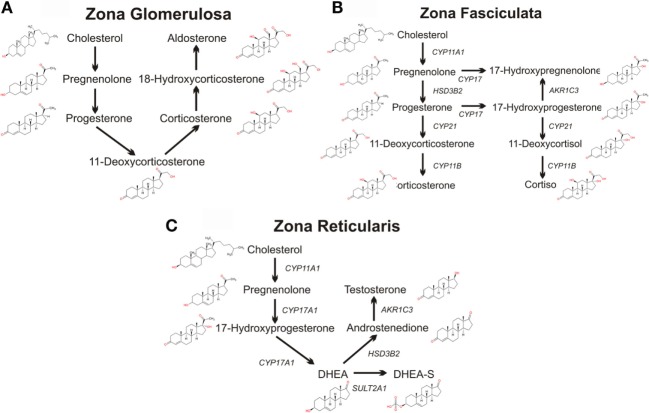
Figure 2.
Schematics of adrenal steroidogenic pathways. The metabolism of cholesterol to pregnenolone by the mitochondrial CYP11A1 is common to all three zones of the human adrenal. (A) The mitochondrial/microsomal enzyme HSD3B converts pregnenolone to progesterone, which is metabolized to 11-deoxycorticosterone by the microsomal CYP21. The final reactions of aldosterone synthesis are catalyzed by the mitochondrial CYP11B2, which converts 11-deoxycorticosterone to corticosterone, which is hydroxylated at C18 to form 18-hydroxycorticosterone which is then finally converted to aldosterone. (B) In the zona fasciculata, the microsomal CYP17 and the mitochondrial/microsomal HSD3B can generate 17-hydroxyprogesterone, progesterone, and 17-hydroxyprogesterone. The microsomal CYP21 preferentially metabolizes 17-hydroxyprogesterone to 11-deoxycortisol, which is finally metabolized to the glucocorticoid cortisol by the microsomal CYP11B2. CYP21 can also metabolize progesterone to 11-deoxycorticosterone, which CYP11B2 converts to the glucocorticoid corticosterone, although this pathway is secondary in humans (although the principal pathway in rodents). (C) In the zona reticularis, CYP17 hydroxylates pregnenolone to 17-hydroxypregnenolone, and then DHEA. DHEA is the major steroid product of the reticularis, with sulfated DHEA (DHEA-S), androstenedione, and testosterone serving as only minor steroidogenic products.