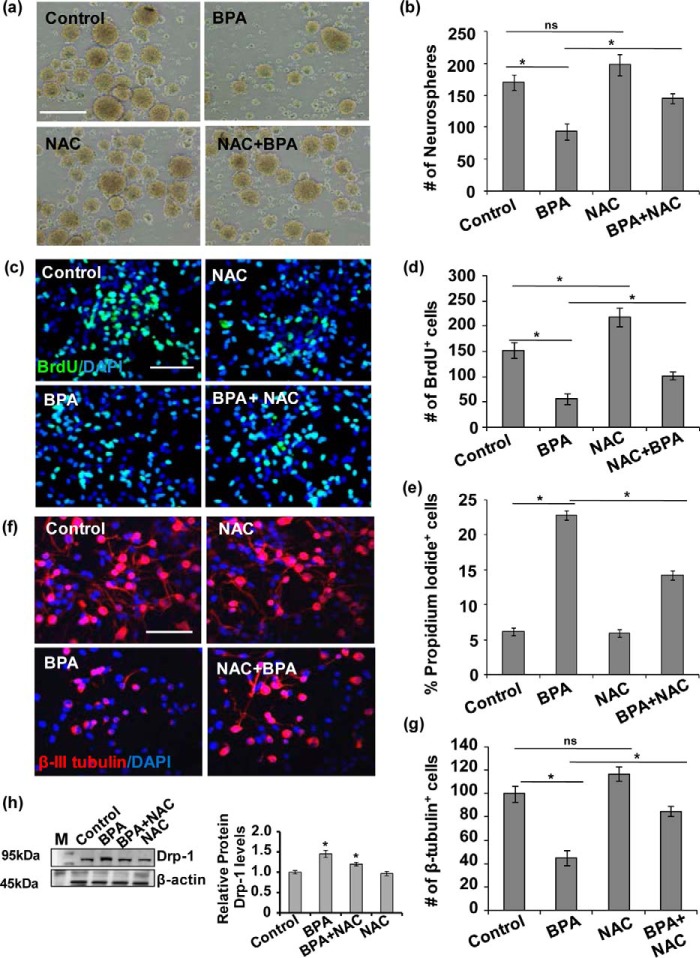
FIGURE 4.
BPA-mediated increased oxidative stress resulted in inhibition of NSC proliferation and differentiation in vitro. a and b, effects of BPA on proliferation of NSC in neurospheres. Neurosphere growth kinetics was done by counting the number of neurospheres. The number and size of NSC-derived neurospheres were decreased by BPA as compared with control. The values are expressed as means ± S.E. (n = 3 cultures). *, p < 0.05. ns, not significant. Scale bar, 100 μm. c and d, primary hippocampal NSC-derived neuronal cultures were treated with BPA (100 μm) in the presence/absence of antioxidant NAC (10 mm), and NSC proliferation was studied by BrdU immunocytochemistry. BPA treatment alters proliferation of the hippocampus NSC in the presence of NAC. Representative immunofluorescent images and quantitative analysis suggested that BPA significantly decreased BrdU+ cells (proliferation marker), but NAC ameliorated the inhibitory action of BPA on proliferation. DAPI was used for counterstaining of the nucleus. The values are means ± S.E. (n = 3 independent experiments). *, p < 0.05. e, the number of apoptotic cells expressed as percentages PI-positive cells as compared with control as studied flow cytometry. The values are expressed as means ± S.E. (n = 3 independent experiments). *, p < 0.05. f and g, BPA treatment also alters neuronal differentiation potential of the hippocampus NSC. Representative immunofluorescent images and quantitative analysis suggested that BPA significantly decreased β-tubulin-III+ neuronal cells (neuronal differentiation marker), but NAC ameliorated the inhibitory action of BPA on differentiation of hippocampus NSC. The values are means ± S.E. (n = 3 independent experiments). *, p < 0.05. ns, not significant. Scale bar, 100 μm. h, Drp-1 protein levels in the presence of NAC in BPA-treated hippocampal NSC-derived neurons culture. The values are means ± S.E. (n = 3 independent experiments). M, marker. *, p < 0.05 versus control.