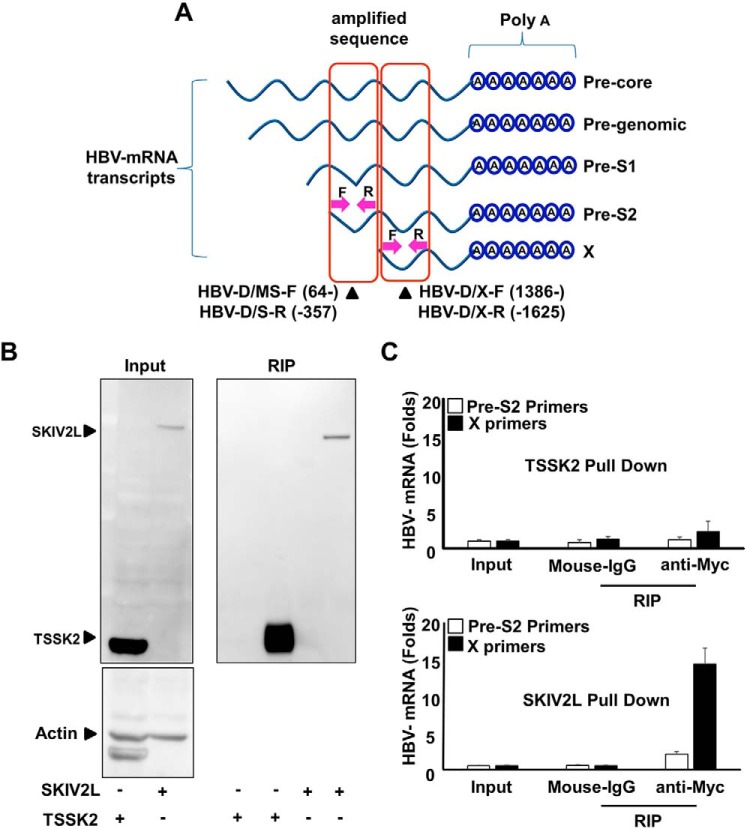
FIGURE 3.
SKIV2L preferentially binds HBV X-mRNA. A, HepG2 cells were transfected with either pEF4-TSSK2-MycHis or pEF4-SKIV2L-MycHis and with HBV-D60 plasmids as indicated. Lysates were extracted at 48 h after transfection. Aliquots (1/10 volumes) were used for the detection of TSSK2, SKIV2L and β-actin (loading control) by immunoblotting (left upper and lower panels); separate aliquots (1/10 volumes) were used for RNA extraction, and the detection of HBV RNA titers by real-time RT-PCR is shown in B. The remaining lysate volumes were subjected to RIP assay using either isotype control antibody (mouse IgG) or mouse anti-Myc IgG to pull down TSSK2-Myc or SKIV2L-Myc proteins. Immunoblotting analysis was performed for the detection of TSSK2 or SKIV2L-Myc in the output samples (right panel). B, HBV mRNA titers in the indicated samples were quantified relative to GAPDH mRNA levels. Three independent experiments were performed in triplicate, and data are presented as the mean ± S.D. C, a diagram representing the sites of the primers used to quantify HBV mRNAs associated with SKIV2L after SKIV2L pulldown by RIP assay. Primers HBV-D/MS-F (64-) and HBV-D/S-R (-357) were used to quantify (collectively) the 4 largest HBV transcripts, including HBV-pg, precore, Pre-S1, and Pre-S2 transcripts; primers HBV-D/X-F (1386-) and HBV-D/X-R (-1625) were used to quantify (collectively) all 5 transcripts, consisting of the above 4 as well as the HBV X mRNA (nucleotide numbering is based on the HBV-ADR sequence). Three independent experiments were performed data are presented as the mean ± S.D.