FIGURE 5.
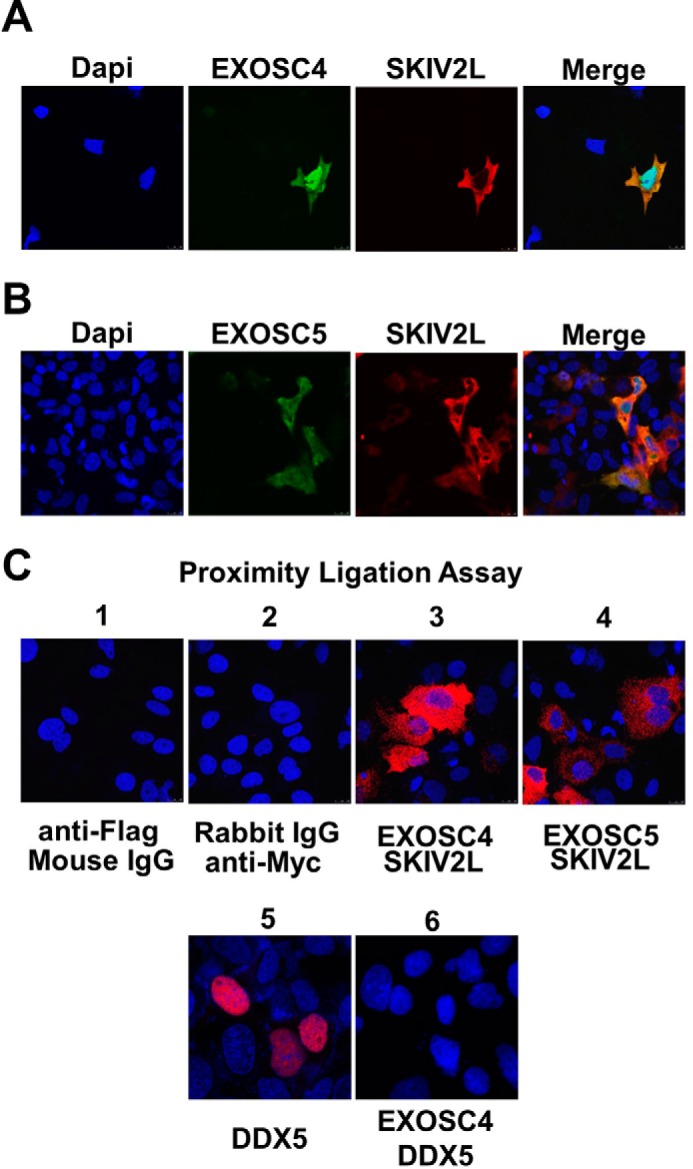
Intracellular localization of SKIV2L/RNA exosome interaction. HuH-7 cells were transfected with pEF4-SKIV2L-MycHis in combination with either pEF-BOS-EXOSC4-FLAG (A) or pEF-BOS-EXOSC5-FLAG plasmids (B). Intracellular localization of SKIV2L-Myc and EXOSC4-FLAG or EXOSC5-FLAG proteins was visualized by immunofluorescence analysis using rabbit anti-SKIV2L and mouse anti-FLAG antibodies. The left panels show the nuclear staining with DAPI (blue). EXOSC4-FLAG and EXOSC5-FLAG intracellular expression was detected by Alexa 488-conjugated secondary antibody (green). SKIV2L intracellular expression was detected using Alexa 555-conjugated secondary antibody (red). The right panels show a merged images of EXOSC4 or 5 (green) with SKIV2L (red) staining C, proximity ligation assay showing the interaction between SKIV2L and EXOSC4 (panel C3) and between SKIV2L and EXOSC5 (panel C4) proteins as red dots. Panels C1 and C2 show the staining observed with combinations of isotype control antibodies; the lack of red staining in these panels confirms that the assay does not detect nonspecific binding. As a control for a nonspecific interaction between over-expressed proteins at the PLA assay, panel C5 shows the nuclear expression of the overexpressed Halo tagged DDX5 helicase using mouse anti-Halo antibody, whereas panel C6 shows no interaction between DDX5 and EXOSC4 protein in PLA assay as evident by the lack of the red dots.
