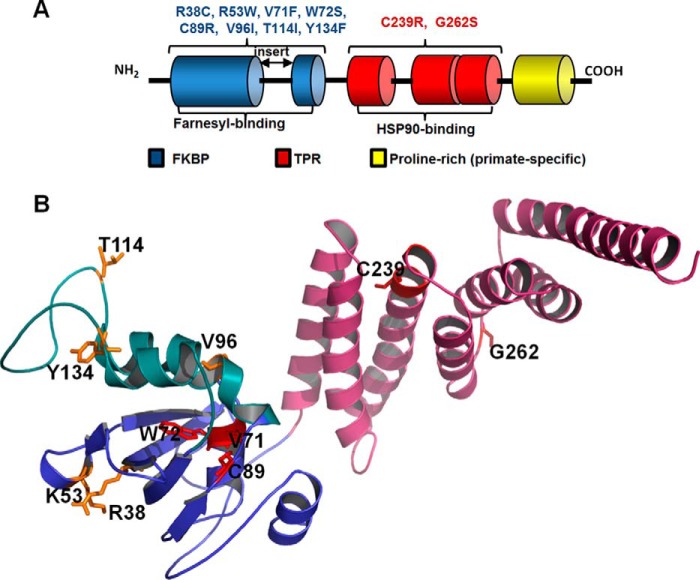
FIGURE 1.
Domains and LCA4 linked mutations of AIPL1. A, schematic representation of the domain structure of AIPL1. All vertebrate AIPL1 proteins consist of an FKBP domain (blue) and a TPR domain with three tetratricopeptide repeats (red). In addition, primate AIPL1 proteins contain a proline-rich region of unknown function (yellow). The “insert” region, which links the last two β-strands in the core FKBP domain, distinguishes the FKBP domains of AIPL1 and AIP from the classical FKBP domain of FKBP12. The FKBP domain of AIPL1 interacts with the prenyl modifications of PDE6, whereas the TPR domain binds HSP90. The diagram indicates which LCA4-linked mutations of AIPL1 were analyzed in this study. B, residues mutated in LCA patients and investigated in this study mapped to the solution structure of mouse AIPL1 (32). Features include the core FKBP domain (blue), the “insert” region (green), and the TPR domain (pink). Residues substituted in AIPL1 mutants that failed to chaperone PDE6 (V71F, W72S, C89R, and C239R) are shown as red sticks; residues substituted in mutant forms that are apparently benign are shown as yellow sticks.