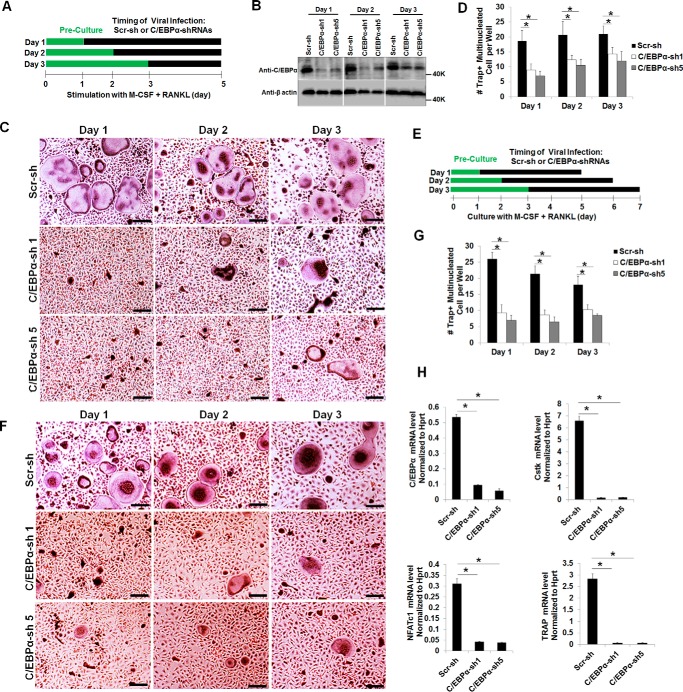
FIGURE 3.
C/EBPα silencing has a stronger impact in the early stage of OC differentiation and drastically suppresses gene expression. A, schematic of the research strategy for B–D. B, MBM cells were infected with a lentivirus encoding scramble shRNA control (Scr-sh) or C/EBPα shRNA constructs 1 or 5 (C/EBPα-sh 1 or 5) on day 1, 2, or 3 of osteoclastogenesis in the presence of M-CSF (10 ng/ml) for 24 h. The cultures were then continued for 5 days with M-CSF alone. Gene expression was examined by Western blotting using β-actin as a loading control. C, the same set of assays as in B were repeated, but cells were infected with a lentivirus for 24 h while undergoing treatment with M-CSF (10 ng/ml) plus RANKL (10 ng/ml) for 5 days. D, quantification for C from at least three independent experiments. E, schematic of the research strategy for F and G. F, MBM cells were infected with a lentivirus encoding Scr-sh or C/EBPα-sh 1 or 5 on day 1, 2, or 3 of osteoclastogenesis with M-CSF (10 ng/ml) and RANKL (10 ng/ml) for 24 h. Following the infection, all cells were cultured with M-CSF (10 ng/ml) and RANKL (10 ng/ml) for 4 days. The cultures in C and F were then stained for TRAP activity. G, quantification for F from three independent experiments. H, MBM cells expressing Scr-sh or C/EBPα-sh 1 or 5 were stimulated with M-CSF (10 ng/ml) and RANKL (10 ng/ml) for 3 days. Gene expression was assessed by qPCR using Hprt as a loading control in three independent experiments. Error bars show averages ± S.D. *, p < 0.05. Scale bars = 200 μm.