Fig. 1.
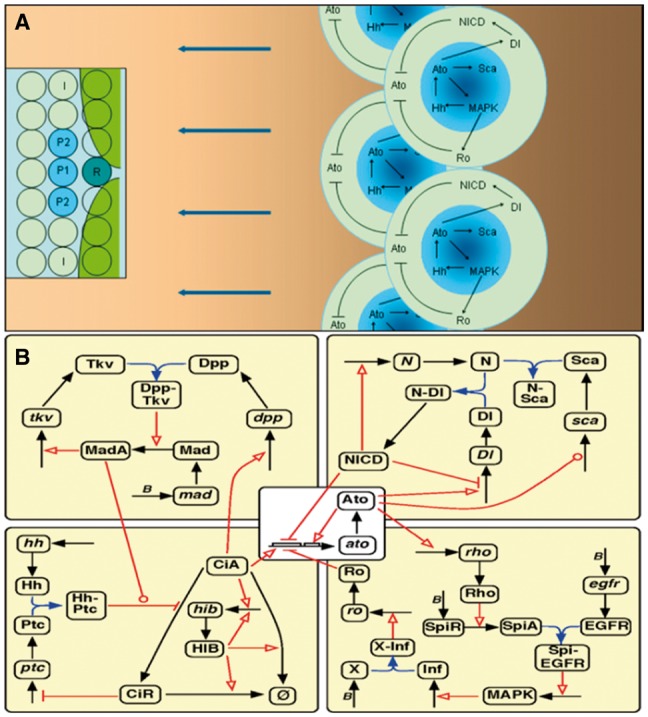
Ato-coordinated Hh, Dpp, Notch and EGFR signaling during R8 patterning. (A) Hh secretion and diffusion drives the anterior (leftward) move of Hh signaling and R8 patterning. Anteriorly diffused Hh causes CiA accumulation, which activates ato in cells anterior to the inhibitory Ro domain (green areas in inset) produced by the last column of (posterior) R8s. Ato induces sca in proneural cells (the dark center of shadowed blue areas) and delta in more cells (shadowed blue areas) to restrain and activate Notch signaling respectively, and induces rho in R8 precursors to activate EGFR/MAPK signaling. EGFR signaling first activates ro in non-R8 cells and later hh in R2/R5 cells. Thus, the Ato-EGFR-Hh-Ato feedback drives the posterior-to-anterior (right-to-left) moving of Hh signaling and R8 fate determination. In the inset R, P1, P2 and I indicate the R8 precursor, proneural cells and intervening cells. (B) The static (canonical) signaling network in each cell. Black and blue arrows indicate the production/degradation of mRNAs/proteins and binding between proteins. Red links indicate proteins’ regulatory functions, those with arrows and bars indicating positive and negative regulation (including transcriptional activation and inhibition), and those with circles indicating more complex regulation. Specifically, that from Ato to sca indicates first activation then inhibition, and that from MadA (Supplementary Table S1) to the red link of HhPtc (Hh-bound Patched) indicates that MadA enhances HhPtc’s function. Letter B indicates basal expression. Hh, Dpp, Sca, SpiA and Inf diffuse into cell. Hh diffuses several ommatidia anteriorly (see panel A) to bind to Ptc and prevents CiA from degrading to the negative CiR. Accumulated CiA induces ato and dpp expression in cells within and anterior to the MF, but is degraded by HIB in cells posterior to the MF. HIB expression is induced by CiA but quickly reaches self-activation, forming a CiA-HIB-CiA negative feedback. Ato induces Rho directly (which represses ro) and Ro indirectly via Rho and EGFR signaling and a diffusible inhibitory factor (Inf, with X as its putative receptor) downstream to EGFR
