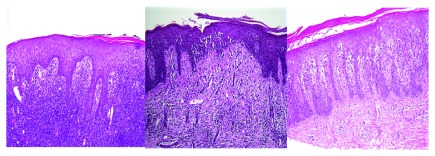
Figure 2. In pathological view, the cutaneous T cell lymphomas are characterized by haloed lymphocytes, exocytosis, epidermotropism, Pautrier’s microabscess, large hyperconvoluted, hyperchromatic lymphocytes in the epidermis, and lymphocytes aligned within the basal layer.
Figure 2A (left) A lymphocytic infiltrate is present in the dermis and extending into the overlying epidermis with minimal overlying spongiosis. Figure 2B (center) Lymphocytes with surrounding haloes are present in the epidermis as single cells and small clusters (Pautrier’s microabscesses). There is minimal accompanying spongiosis. Figure 2C (right) Psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia with epidermotropism of haloed lymphocytes is seen in this case of patch-stage mycosis fungoides.