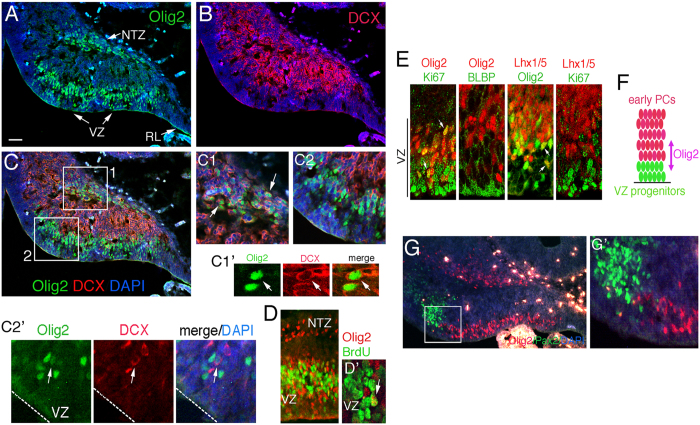
Figure 1. Differential neuronal expression patterns of Olig2+ cells in the early embryonic cerebellum.
Co-immunostaining is performed to analyze the expression of Olig2 (A) and a neuronal marker, DCX (B) on sagittal sections of the E12.5 cerebellum. The overlay image (C) reveals differential DCX expression patterns of the Olig2+ cells in the VZ and NTZ. The enlarged images of the boxed regions in (C) are shown in (C1) and (C2), respectively. Double-positive cells are pointed by arrows in (C1) and an arrow in a higher power confocal image (C1’). Double-positive cells (indicated by an arrow in C2’, a higher power confocal image of C2 region) are very rarely seen in (C2) where Olig2 and DCX show mostly a non-overlapping staining pattern. (D) Co-immunostaining of Olig2 and BrdU in the VZ of the E12.5 cerebellum that has been treated by a BrdU pulse-labeling. (D’) The confocal image of the VZ in (D) showing a double-positive cell (arrow). (E) Co-expression analysis of Olig2 with markers of proliferation (Ki67), radial glia (BLBP) and PC differentiation (Lhx1/5) in the cerebellar VZ at E13.5. (F) A diagram depicting Olig2 expression range during the transition of VZ progenitors to early PCs. (G) Co-immunostaining with anti-Olig2 and anti-Pax2 on sagittal cerebellar sections of the E13.5 wild-type mouse. (G’) is the enlarged image of boxed regions in (G) showing a non-overlapping staining pattern. VZ, ventricular zone; RL, rhombic lip; NTZ, nuclear transitory zone. Scale bar: 80 μm in A,B,C and G; 25 μm in C1 and C2; 15 μm in C1’ and D’; 20 μm in C2’, E and G’; 40 μm in D.