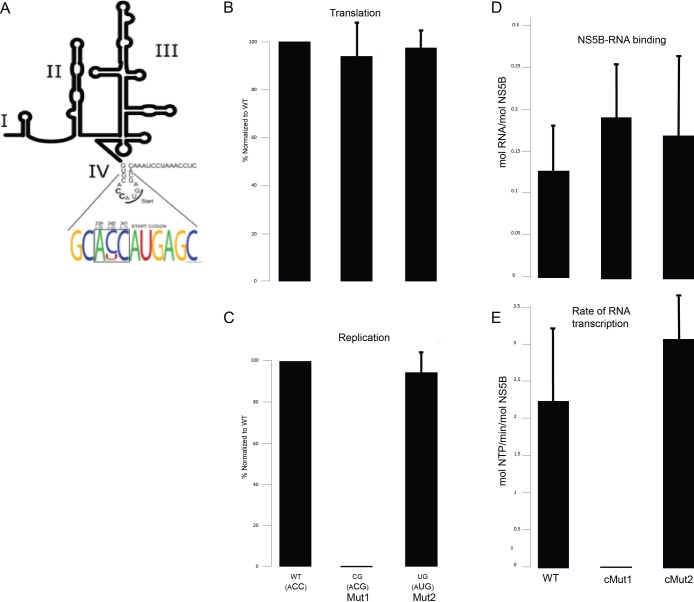
Figure 6.
Membrane-associated HCV replicase assays with mutant RNA templates identifies transcriptional defect associated with impaired HCV RNA genome replication. (A) Weblogo analysis indicating a high degree of conservation at positions −2 and −1 from the AUG translational start site codon in the Kozak consensus sequence in the plus (+) RNA strand of a large collection of HCV isolates. (B) Effect of mutation at positions −2 and −1 to CG (Mut1) or UG (Mut2) on HCV translation. (C) Effect of mutation at positions −2 and −1 to CG (Mut1) or UG (Mut2) on HCV RNA genome replication. (D) NS5B-FL was immobilized on lipid bilayer membranes as shown in previous figures. Wild type or mutant (cMut1 or cMut2, which contain mutations in the minus (−) strand cIRES RNA complementary to Mut1 and Mut2, respectively) cIRES RNA templates were bound as shown in Figure S7C. (E) RNA-dependent RNA transcription activity (mol NTP/min/mol NS5B) observed upon subsequent addition of ribonucleoside triphosphates (NTPs), as in Figure S7.