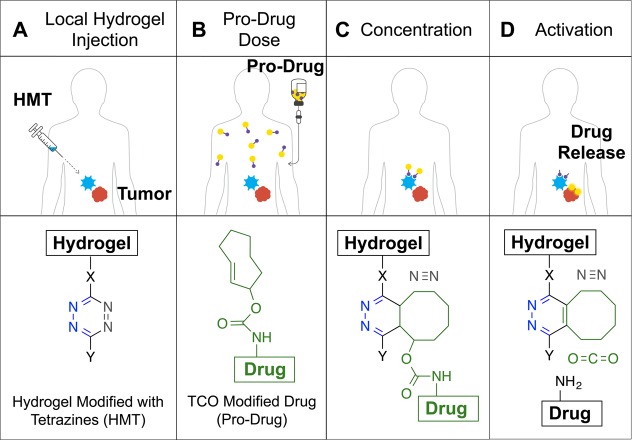
Figure 2.
In vivo bioorthogonal chemistry for the concentration and activation of systemic pro-drugs. (A) A hydrogel modified with Tz (HMT) is injected into the area where the drugs are needed. (B) A drug covalently modified with a TCO carbamate (pro-drug) is given to the patient. (C) When the pro-drug and the material come in contact, the rapid cycloaddition reaction enhances the amount of drug present at the desired location with the concomitant release of a molecule of nitrogen. (D) The resulting cycloadduct isomerizes in vivo leading to decomposition of the self-immolable carbamate linker, releasing an equivalent of carbon dioxide and most importantly the drug at the local site to perform its therapeutic function.