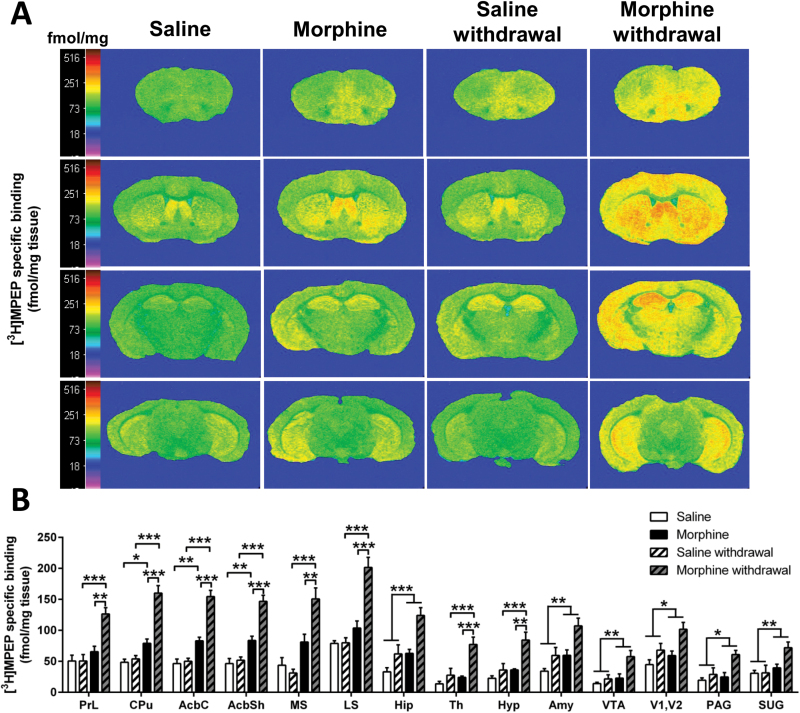
Figure 3.
Morphine withdrawal increases metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGlu5R) binding in the brain. (A) Representative autoradiograms of 10 μΜ [3H]-2-methyl-6-([3,5-3H] phenylethynl) pyridine ([3H]MPEP) binding to mGlu5R in coronal brain sections of mice undergoing chronic saline or morphine administration and 7-day withdrawal. Autoradiograms of brain sections were taken at the level of prefrontal cortex (Bregma: 2.34mm; first row), striatum (Bregma: 0.62mm; second row), thalamus (Bregma: -1.82mm; third row), and ventral tegmental area (Bregma: -3.40mm; fourth row). Binding levels are represented using a pseudocolor interpretation of black and white film images in fmol/mg of tissue equivalent. (B) Quantitative mGlu5R binding in the brain of mice subjected to morphine administration and withdrawal. Data are expressed as the mean±SEM (n=6–7/group). *P<.05, **P<.01, ***P<.001 (2-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test per brain region).