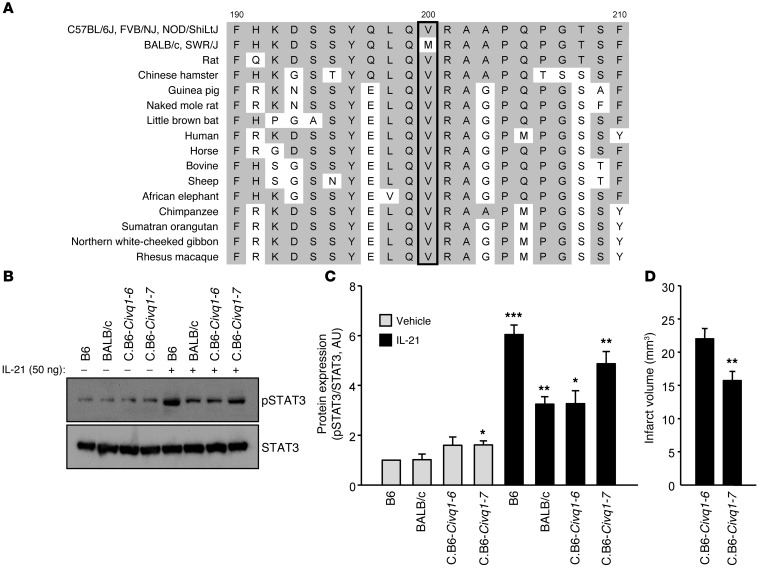
Figure 5. Functional consequences of IL-21R are altered by a second IL-21R coding difference between inbred mouse strains.
(A) Alignments of amino acid sequences are compared across different inbred mouse strains and other mammalian species. The valine (V) found at amino acid position 200 (rs33006504) in B6, FVB, and NOD mouse strains is well conserved in mammalian species except inbred mouse strains BALB/c and SWR showing the methionine (M) at the amino acid position. This V200M change is predicted to be functionally damaging to the protein with in silico analysis (PolyPhen-2 score: 0.789). (B) Western blots were performed to detect levels of both p-STAT3 and STAT3 in explanted brain slices of 2 inbred mouse strains, B6 and BALB/c, as well as 2 Civq1 congenic lines, C.B6–Civq1–6 and C.B6–Civq1–7, 1 hour after treatment with either vehicle or recombinant murine IL-21 (50 ng/ml). (C) Levels of p-STAT3 were determined. Level of total STAT3 was used for normalization. Experiments were performed 3 times using 3 mice per mouse strain for each experiment. Values represent mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 vs. B6 vehicle treatment, 2-tailed Student’s t test. (D) Graph shows the infarct volume. Total numbers of animals for C.B6–Civq1–6 and C.B6–Civq1–7 are 29 and 30, respectively. Representative images are shown in Supplemental Figure 13, F and G. Values represent mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01 vs. C.B6–Civq1–6, 2-tailed Student’s t test.