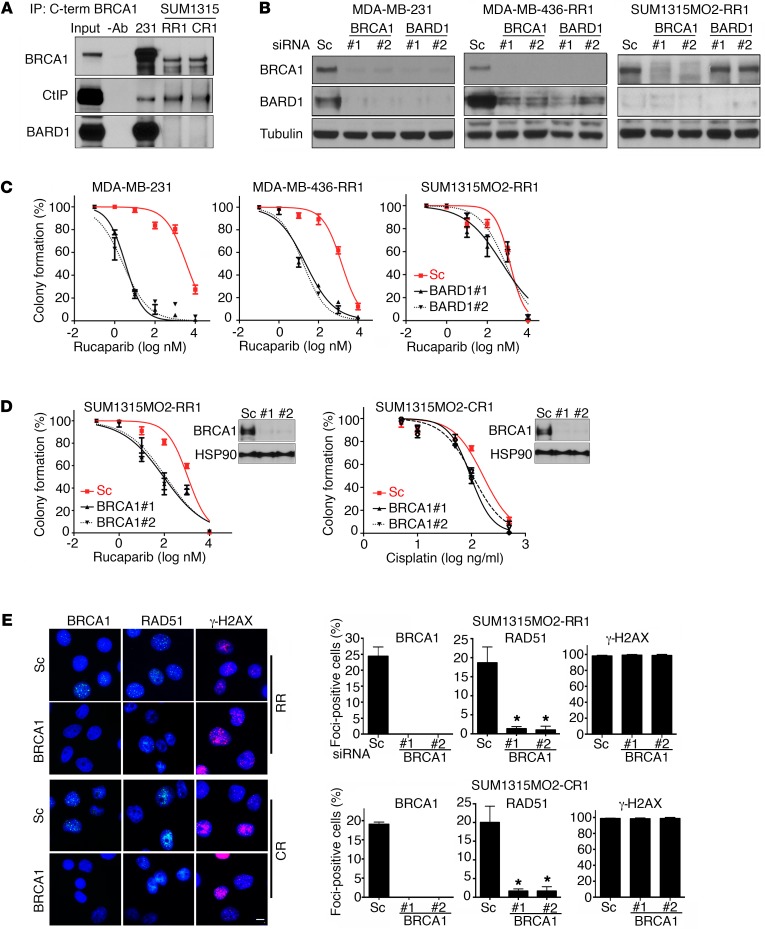
Figure 3. Rdd-BRCA1 does not require BARD1 for stability or function.
(A) BRCA1 was immunoprecipitated from MDA-MB-231 and SUM1315MO2 RR1 and CR1 cells using a C-terminal–specific Ab. Immunoprecipitates were measured for BRCA1, BARD1, and CtIP protein levels by Western blot analysis. Three independent experiments were performed. (B) MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-436-RR1, and SUM1315MO2 RR1 cells were treated with scrambled (Sc) or 2 independent siRNAs targeting BRCA1 or BARD1, and BRCA1, BARD1 and tubulin measured by Western blot analysis. Samples were run on parallel gels. The tubulin blot was derived from duplicate samples run on a parallel gel. (C) Cells described in B were transfected with scrambled or 2 independent BARD1 siRNAs, treated with increasing concentrations of rucaparib, and colony formation assessed. (D) Cells were transfected with scrambled, BRCA1 no. 1, or BRCA1 no. 2 siRNA, followed by treatment with increasing concentrations of either rucaparib or cisplatin for either SUM1315MO2 RR1 or CR1 cells, respectively, and then reseeded for colony formation assay (n = 3). Insets show Western blots of BRCA1 knockdown. Three independent experiments were performed. (E) SUM1315MO2 RR1 and CR1 cells were treated with scrambled or 2 independent BRCA1 siRNAs and subjected to IR. BRCA1, RAD51, and γ-H2AX IRIF were assessed by immunofluorescence. Representative images are shown. Scale bar: 10 μm. Bar graphs show the mean and SEM percentage of cells containing more than 5 foci (n = 3 independent experiments; *P < 0.05, 2-tailed Student’s t test).