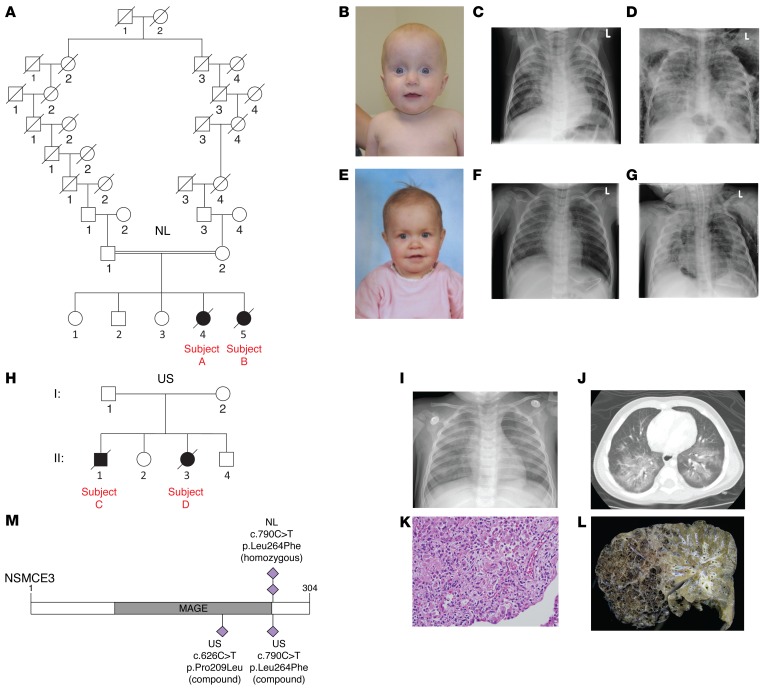
Figure 1. Affected individuals with NSMCE3 mutations with severe lung disease immunodeficiency and chromosome breakage syndrome (LICS).
(A) Pedigree of family 1. (B) Facial appearance of affected individual A (note the thin skin and prominent veins). (C) Chest X-ray of individual A, 4 days before admission at the PICU, showing severe PARDS consisting of bilateral alveolar infiltrates and (D) 14 days after admission, showing diffuse interstitial and alveolar infiltrates, pneumomediastinum, and subcutaneous emphysema. (E) Facial appearance of affected individual B. No dysmorphic facial features were noted. (F) Chest X-ray of individual B on admission at the PICU showing a predominantly right-sided alveolar infiltrate and (G) 18 days after admission showing severe PARDS complicated by pneumomediastinum, pneumothorax, and subcutaneous emphysema. (H) Pedigree of family 2. (I) Chest X-ray showing bilateral interstitial infiltrates of affected individuals C and D. (J) Corresponding chest CT scan at the level of the carina showing bilateral ground glass haziness with areas of consolidation and interposed air bronchogram. (K) Lung biopsy of individual D at day 6 showing patchy acute interstitial infiltrates with lymphocyte predominance. In the areas of parenchymal injury, there was marked alveolar epithelial hyperplasia, consistent with early diffuse alveolar damage (original magnification, ×400). (L) Lung explant showing significant damage that includes overinflation, macroscopic cystic changes, and intracystic hemorrhage. (M) Schematic representation of the NSMCE3 protein with the identified missense mutations of the affected individuals. The homozygous mutations from the affected individuals from the Netherlands (NL; A and B) are indicated above and the compound heterozygous mutations from the affected individuals from the United States (US; C and D) are depicted below the figure.