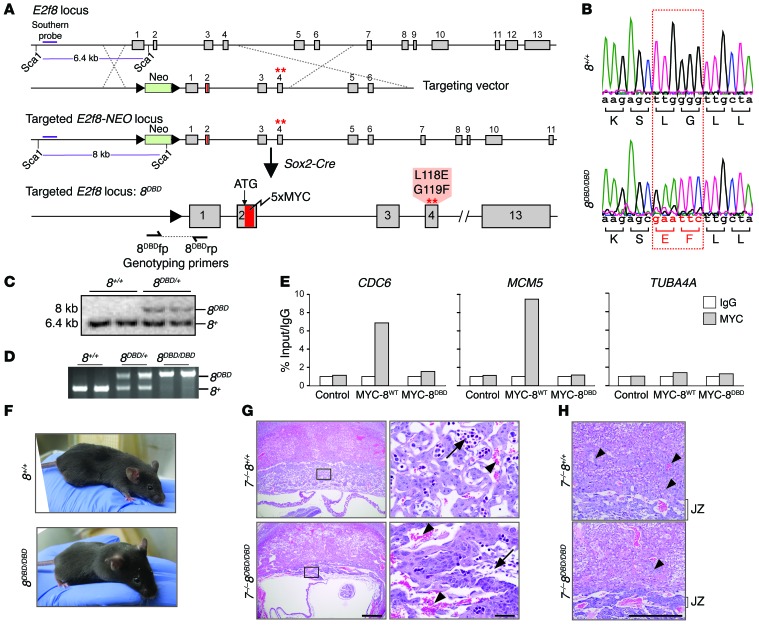
Figure 4. DNA binding activity is required for E2F8 function during development.
(A) Diagram of the mouse E2f8 locus, targeting vector, and targeted E2f8 locus prior to and after germ line deletion of the neomycin (NEO) cassette using Sox2-Cre. A 5×MYC tag (red) was inserted after the ATG and the first DNA binding domain (DBD1) was mutated; amino acid changes are noted. Dashed lines show homologous recombination between targeting vector and endogenous locus. The purple line represents the Southern probe used to test embryonic stem (ES) cell clones after Sca1 digestion. (B) Sequencing histogram of wild-type (8+/+) and 8DBD/DBD mice showing the mutation in DBD1 of E2f8. Altered nucleotides and resulting amino acid changes are shown in red. (C) Southern blotting for the E2f8+ and E2f8DBD alleles in ES cells. (D) PCR genotyping of DNA from 8+/+, 8DBD/+, and 8DBD/DBD mice using primers flanking the LoxP site shown in A. The 8DBD (320 bp) and 8+ (209 bp) bands are noted. (E) ChIP-qPCR using IgG or MYC antibodies in HepG2 cells (control) or HepG2 cells expressing 5×MYC-tagged wild-type E2F8 (MYC-8wt) or 5×MYC-tagged DBD E2F8 (MYC-8DBD). CDC6 and MCM5 are established E2F targets; TUBA4A is shown as a negative control. Percentage of input values for MYC-tagged E2F8 were normalized to IgG. (F) Pictures of 8+/+ and 8DBD/DBD mice. (G) H&E-stained sections from E10.5 7–/– 8+/+ and 7–/– 8DBD/DBD placentation sites illustrating altered placental architecture with a disruption in fetal capillary formation and pooling of maternal blood in 7–/– 8DBD/DBD placentas. Arrows, fetal blood vessels. Arrowheads, maternal blood sinuses. Scale bars: 500 μm (left) and 50 μm (right). (H) Higher magnification of sections from G illustrating altered placental architecture with compaction of the placental junctional zone (JZ) and limited trophoblast invasion (arrowheads) in 7–/– 8DBD/DBD placentas. Scale bar: 500 μm.