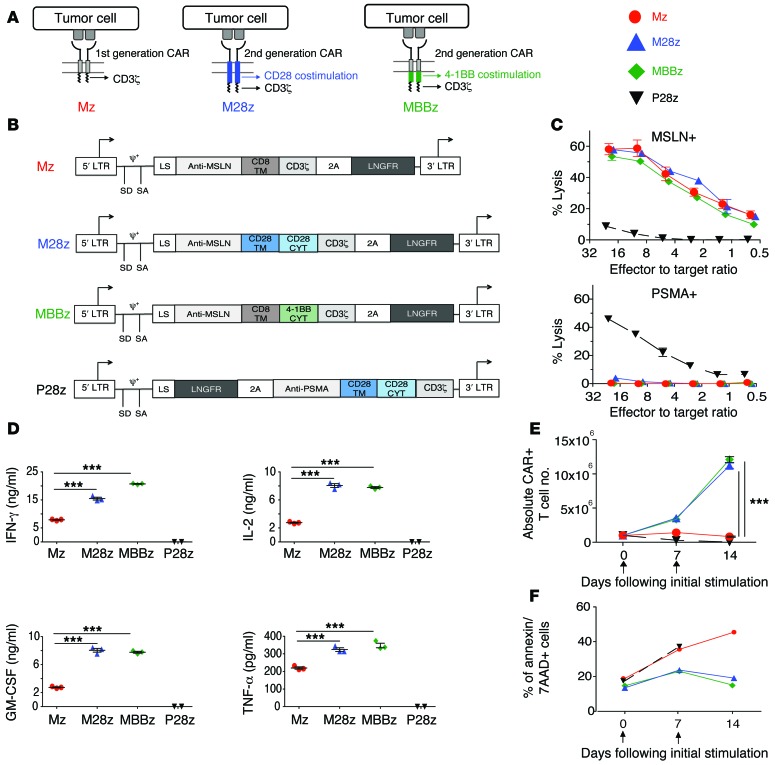
Figure 1. CARs with CD28 or 4-1BB costimulation exhibit similar cytolytic functions, effector cytokine secretion, and proliferation in vitro upon initial antigen stimulation.
(A) First- and second-generation CARs. (B) MSLN–targeted CARs contain the CD3ζ endodomain either alone (Mz, first-generation CAR) or in combination with the CD28 (M28z) or 4-1BB (MBBz) costimulatory domain (second-generation CAR). PSMA-directed CARs with CD28 costimulation (P28z) as well as PSMA-expressing targets (PSMA+) are included in experiments as negative controls. CYT, cytoplasmic domain; LS, leader sequence; LTR, long terminal repeat; SA, splice acceptor; SD, splice donor; TM, transmembrane. (C–E) Antigen-specific effector functions of CAR-transduced T cells. (C) Lysis of MSLN-expressing targets (MSLN+), but not PSMA+ targets, as measured by chromium-release assays. (D) 4-1BB and CD28 costimulations enhance cytokine secretion, as assessed by Luminex assay, after coculture of CAR T cells with MSLN+ cells. (E) M28z and MBBz CARs facilitate robust T cell accumulation after stimulation with MSLN+ cells. (F) 4-1BB and CD28 costimulations decrease the rate of apoptosis as assessed by annexin V/7-AAD+ staining every 7 days after coculture with MSLN+ target. (D and E) ***P < 0.001, comparing costimulated CAR T cells (M28z or MBBz) with the first-generation receptor (Mz), by Student’s t test; significance was determined using the Sidak-Bonferonni correction for multiple comparisons. Data are representative of at least 3 independent experiments and represent the mean ± SEM (C and E) of 3 replicates or are plotted as individual points.