Figure 3.
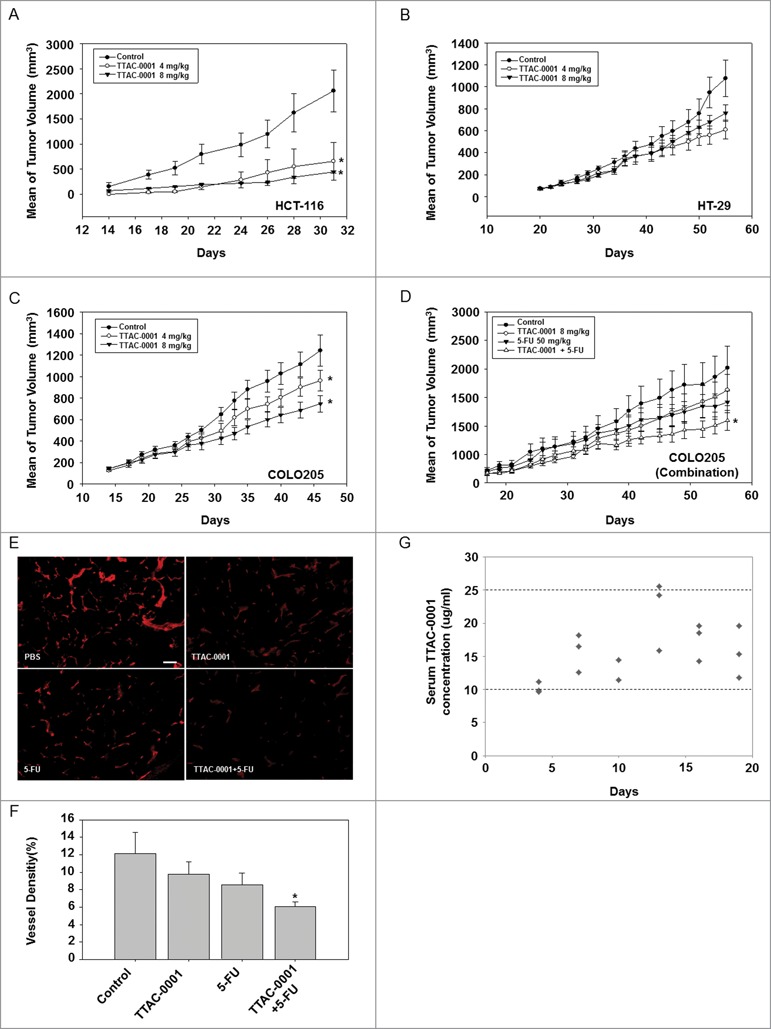
TTAC-0001 inhibits tumor growth of transplantable human colon cancer cells in BALB/c-nu mice. Tumor growth curves of transplantable human colon carcinomas in female BALB/c-nu mice. (A−C) Mice were inoculated subcutaneously in the right flank with human colon cancer cells HCT-116, COLO205, or HT-29. Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) or 4 or 8 mg/kg TTAC-0001 were injected intravenously once per week. Tumor sizes were measured 3 times per week using a caliper (mean ± SE, n = 8). (D) Combination treatment of TTAC-0001 and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) leads to greater tumor volume reduction. Mice were given injections of PBS, TTAC-0001, 5-FU, or 5-FU + TTAC-0001 (Mean ± SE, n = 8). * p< 0.05 vs. control. (E) Immunohistofluorescence analysis of CD31-positive blood vessels (red) in the xenograft tumor. Scale bars = 200 µm. (F) Densities of CD31-positive blood vessels in the xenograft tumor (VD = vessel density; n = 8; * p < 0.05 vs. control). (G) Relationship between serum TTAC-0001 concentration and efficacy in COLO205 tumors. TTAC-0001 concentrations were measured in serum every 3 d. Mice were intravenously administered 8 mg/kg TTAC-0001, once per week.
