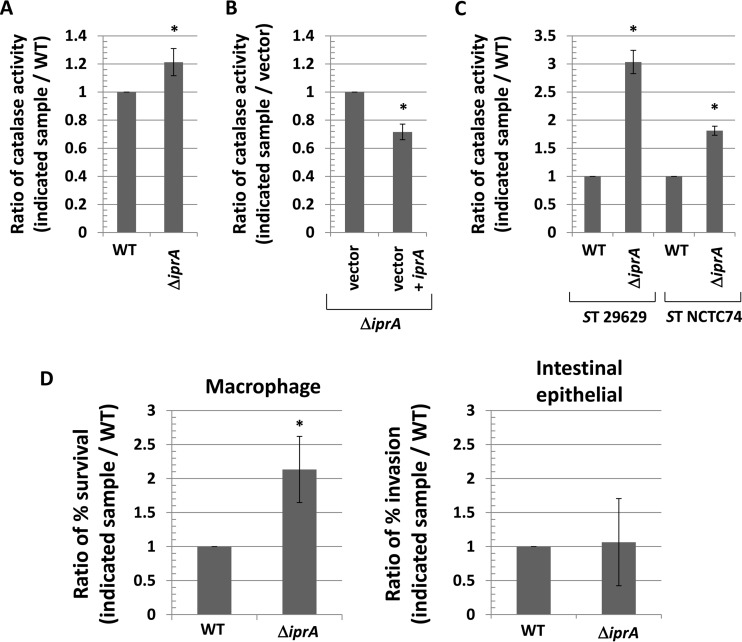
FIG 3.
Increased catalase activity and survival in macrophages associated with ΔiprA mutation in S. Typhimurium. (A) S. Typhimurium χ3339 WT and χ3339 ΔiprA mutant strains were measured for catalase activity, and a ratio of the activity in each sample to the WT value was calculated and plotted. (B) S. Typhimurium χ3339 ΔiprA mutant strains containing plasmid vector or vector plus iprA were measured for catalase activity, and a ratio of the activity in each sample compared to the vector strain activity was calculated and plotted. (C) S. Typhimurium strains 29629 and NTCT74 containing ΔiprA mutations were compared to each corresponding WT for catalase activity. (D) S. Typhimurium strain χ3339 WT and ΔiprA mutant strains were used to infect J774 macrophage cells and Int407 intestinal epithelial cells, and the percent survival (in macrophages) and percent invasion (for intestinal epithelial cells) were measured for each strain at 2 h postinfection. A ratio of these values for each sample to the values for the WT was calculated and plotted. Data in each panel are shown as the mean plus standard deviation, and observed differences from the WT were found to be significant (as indicated by an asterisk) at a P value of <0.05 using a t test to compare the WT and the indicated mutant sample or, for panel B, the vector and the vector plus iprA.