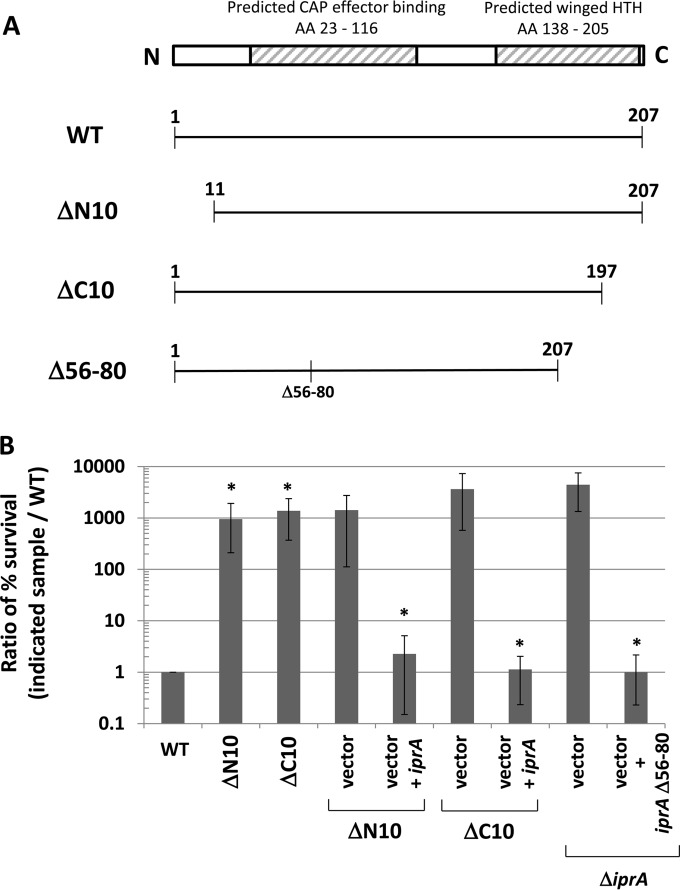
FIG 5.
Deletion of IprA protein regions. (A) Diagram of WT IprA protein and the ΔN10, ΔC10, and Δ56-80 mutant derivatives constructed in S. Typhimurium for this study. The ΔN10 and ΔC10 alleles remove the first 10 amino acids (AA) from the N terminus and last 10 amino acids from the C terminus from S. Typhimurium IprA, respectively. The Δ56-80 allele contains a deletion of amino acids 56 to 80 located in the predicted CAP effector binding domain of the S. Typhimurium IprA protein. The ΔN10 and ΔC10 alleles were constructed in the chromosome, and the Δ56-80 allele was constructed in a plasmid. (B) S. Typhimurium strain χ3339 containing either the ΔN10 or ΔC10 mutation was tested for oxidative stress survival and compared to the isogenic WT strain, as described for previous experiments. The same mutant strains containing plasmid vector and vector plus iprA were also tested for oxidative stress survival and compared to the WT. The χ3339 ΔiprA mutant strain containing plasmid vector or vector plus the iprA Δ56-80 mutant was tested for oxidative stress survival in the same manner as the other strains. Data are shown as the mean plus standard deviation, and observed differences were found to be significant (as indicated by an asterisk) at a P value of <0.05 using a t test to compare either the WT and the indicated mutant or the vector and the vector plus iprA, as indicated.