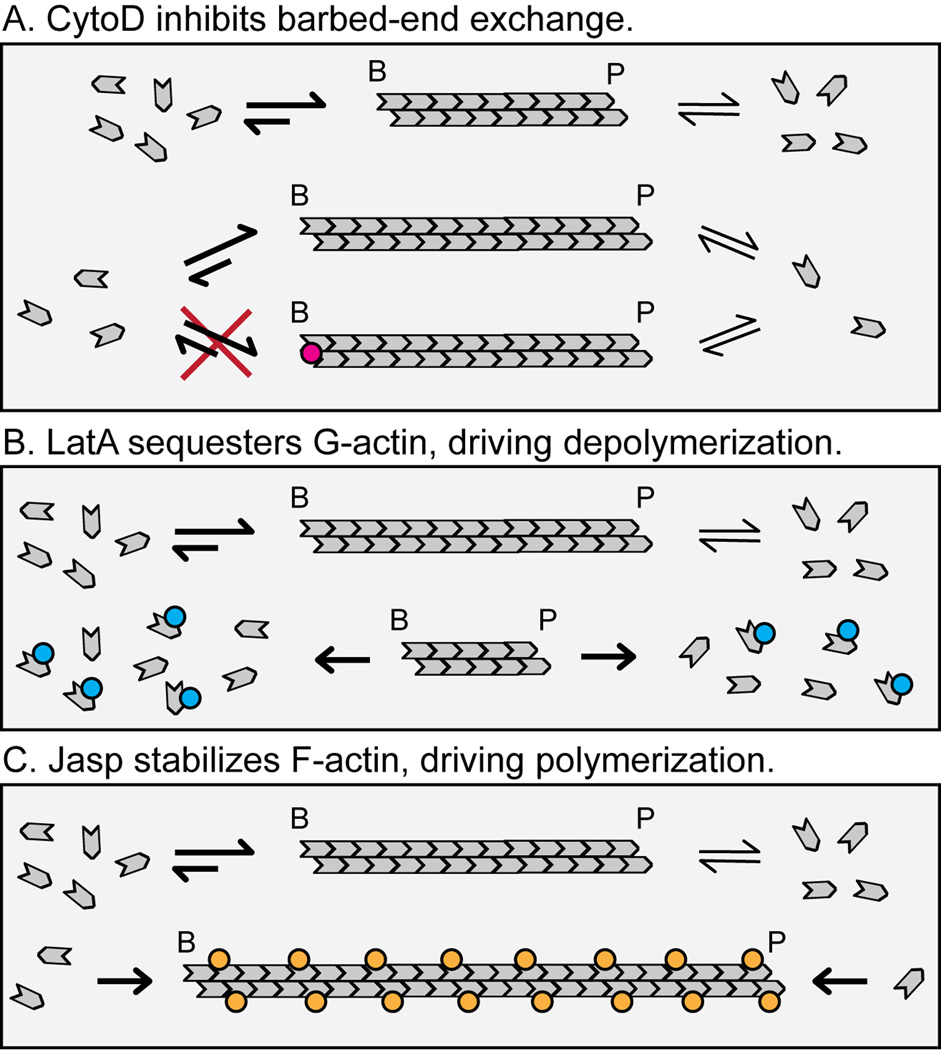
Figure 2. Effects of actin-disrupting drugs on actin filament assembly.
(A) CytoD inhibits barbed-end assembly of actin monomers. (B) LatA sequesters actin monomers, driving the F:G-actin balance toward the G-actin state [50]. LatA function requires that the actin filament be dynamic (i.e., capable of exchanging subunits with the G-actin pool). (C) Jasp stabilizes actin filaments, driving the F:G actin balance toward the F-actin state. The depicted distribution of Jasp along the actin filament is speculative and does not reflect known distributions or stoichiometries of Jasp required for filament stabilization in vitro or in vivo. Jasp competes with phalloidin for F-actin binding in vitro [51], and one phalloidin molecule can bind each subunit within F-actin under saturating conditions [52]. Thus, Jasp may recognize the same F-actin binding site as phalloidin with a similar stoichiometry, but this has not been proven.